Multiple Choice:
1. Which of the following statement(s) about monopoly regulation is correct?
a. Rate of return regulation allows regulated firms to earn unlimited amount of revenue above cost
b. Earnings Sharing regulation allows regulated firms to retain fixed amount of the gains they create
c. Price Caps regulation attempts to make the price the monopolist can charge independent of cost reduction
d. It has been easy to find comparable utilities to set up prices for Yearstick regulation
2. The traditional organization of the U.S. electric power industry is ______.
a. vetically intergated
b. a single regulated firm (IOUs) provides all generation, transmission, and distribution functions
c. Investor-owned utilities provide exclusive services to certain retail customers and are regulated by state regulatory commissions
d. All of the above
3. In the so-called consumer choice model (or retail competition) illustrated in the following figure, which of the statement(s) is true?
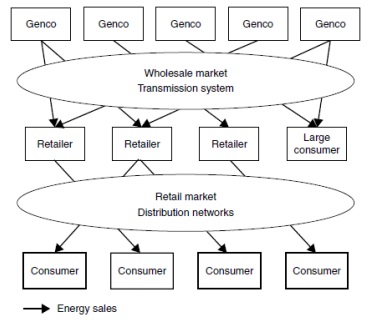
a. Only large consumers can choose their suppliers
b. The only remaining monopoly functions are the operation of the transmission and distribution networks
c. The retail price has to be regulated
d. The whole-sale competition model creates more competition for retail consumers than this model
4. The reasons for the large wholesale price increase during the California Energy Crisis include _____.
a. the rising production cost of natural gas and emission credits
b. Imported hydroelectric power was significantly less
c. the exercising of market power by wholesale power producers
d. all of the above
5. When Ramsey pricing is applied to a multiproduct natural monopolist, _________.
a. firm’s total revenue covers the total cost
b. the deadweight losses are minimized
c. the prices are raised in inverse proportion to demand elasticities of corresponding products
d. all of the above
Short Answer:
6. Assume that an electricity monopoly serves two consumer types, industrial and residential. The demands by the two classes are as follow. Industrial: Q1 = 30 - P1 and Residential: QR = 20 - 0.5PR . The company has the cost function in the form of C = 148 + 5Q1+ 5QR . Find the Ramsey prices and quantities.
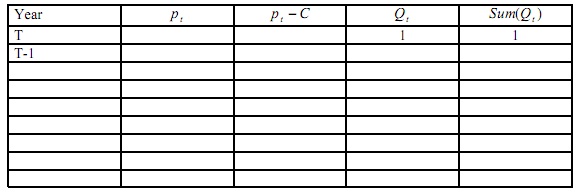
7. Suppose we own a coal mine, which as total stock of 153 tons. Demand in each year is Qt = 100 - pt (Q is in tons and P is in $/ton). Assume that marginal cost of extraction is $10 , interest rate r = 10%, and exactly 1 ton is sold in the last year of production (t = T). Based on Hotelling model, during how many periods does extraction take place? What is the price in the initial period? (You may use the table below to answer the question)
8. In class, we discussed a simple two-period model of dynamically efficient extraction of a nonrenewable resource with a finite stock of Q units, constant extraction costs of C, and constant demand given by the inverse demand function: Pi = a - bqi, i = 1,2. Assume the interest rate is r.
i) Solve for the socially optimal quantity of resource extraction in both periods (as functions of the constants, Q,C,a,b,and r)
ii) Assume that a = 10, b = 0.5, c = 3,r = 10%, and Q = 20. Sovle for the optimal extractions and equilibrium rpices in both periods.
iii) If we change the interest rate from 10% to 15%, what are the optimal extractions in both periods? Compare the optimal extractionsin (2) and (3). Explain the logic (intuition) behind the difference.
iv) What would be the optimal extractions if we extend from two to three periods (keep all parameters the same as in (2))
9. Now we change the situation in Q1 in the following manner. We know in period 1 that due to technological change, the dmeand for the resource will decrease in period 2. Hence, there are now different demand functions for each period, which are:
P1 = 10 - 0.5q1
P2 = 8 - 0.5q2
The other parameters are the same as in Q1-(2): C = 3, r = 10%, and Q = 20.
i) What are the optimal quantity of extraction in the two periods?
ii) Compare the optimal extraction in period 1 to the answer in Q1-(2). Explain the logic (intuition) behind the difference.
iii) What is the marginal user cost or scarcity rent in the two periods?