Question 1: GDP
a) State concisely, in your own words, the essence:
i) Of what GDP measures and
ii) What GDP doesn’t measure?
b) Stocks and bonds issued by firms comprise the ‘Investment’ component of GDP.
i) True or False?
ii) Briefly describe why.
c) It is pretty much a given, through time and across countries, that Consumption accounts for about 70% of GDP.
i) True or False?
ii) Briefly describe why.
d) A March 2012 article in the WSJ observed, ‘It was the first increase [in household debt] as the second quarter of 2008, before Lehman Brothers’ collapse and the ensuing financial panic and recession. As then, Americans have focused on decreasing their debt. That procedure strengthens an economy in the long run however crimps short-term growth.
{Excerpt from Neil Shah, “Consumers Shape Up Their Finances,” The Wall Street Journal, March 9, 2012, pA2.}
How does that work … those households reducing debt strengthens an economy in the long run but “crimps” it in the short term?
e) If you only get to know either the nominal or real GDP growth rate of an economy,
i) Which would you select?
ii) Why?
f) Briefly describe whether you
i) Agree or disagree with the following statements and
ii) Why?
• “If nominal GDP is less than real GDP, then the price level must have fallen during the year.”
• “Whenever real GDP declines, nominal GDP must also decline.”
• “If a recession is so severe that the price level declines, then we know that both real GDP and nominal GDP must decline.”
• “Nominal GDP declined between 2008 and 2009, therefore the GDP deflator must also have declined.”
g) An artist buys scrap metal from a local steel mill as a raw material for her metal sculptures. Last year, she bought $5,000 worth of the scrap metal. Throughout the year, she produced 10 metal sculptures which she sold for $800 each to a local art store. The local art store sold all of the sculptures to local art collectors, at an average price of $1,000 each.
For the 10 metal sculptures,
i) What was the total value added of the artist, and
ii) What was the total value added of the local art store (Show work and describe each point)?
Question 2: Economic Growth
a) Referring to the table below and by using the Rule of 70, comment on long-term changes in the standard of living in the United States?
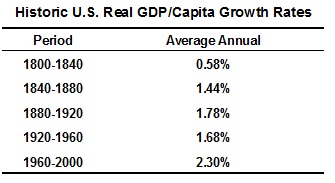
b) Would you rather live in the United States of 1900 with an annual income of $1million or in the United States of 2012 with an annual income of $50,000? (Both incomes are begun in 2012 dollars).
Briefly show and describe why?
c) Increases in real GDP per capita depend on increases in labor productivity. What drives labor productivity?
d) In developed economies, economic growth depends more on technological change than on increases in capital per hour worked. What drives technological change?
e) Briefly, what crucial role can/should government play to foster the long-term economic growth?
f) An economy – by definition – is always operating at potential GDP.
i) True or False?
ii) Briefly describe why?
g) In a closed economy, or in an economy where net exports are zero (NX = 0), total Savings should equal total Investment (S = I).
i) True or False?
ii) Why?
h) If the government runs a balanced budget, where does all of S (National Savings), come from?
i) The article quoted from in question 1d referred to a general de-levering of the U.S. household. It follows, then, that the US economy as a whole must be de-levering. True or False? Why?