Solve the following:
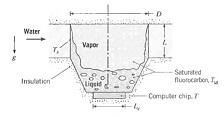
Q: A novel scheme for cooling computer chips uses a thermosyphon containing a saturated fluorocarbon. The chip is brazed to the bottom of a cuplike container within which heat is dissipated by boiling and subsequently transferred to an external coolant (water) via condensation on the inner surface of a thin-walled tube.
The nucleate boiling constants and the properties of the fluorocarbon are provided in Problem 10.23. In addition k, = 0.054 W/m · K.
(a) If the chip operates under steady-state conditions and its surface heat flux is maintained at 90% of the critical heat flux, what is its temperature T? What is the total power dissipation if the chip width is Lc = 20 mm on a side?
(b) If the tube diameter is D = 30 mm and its surface is maintained at Ts = 25°C by the water, what tube length L is required to maintain the designated conditions?