Assignment:
Production and Operations Management
Q1. An assembly line with 17 tasks is to be balanced. The longest task is 2.4 minutes, and the total time for all tasks is 18 minutes. The line will operate for 450 minutes per day.
- What are the minimum and maximum cycle times?
- What range of output is theoretically possible for the line?
- What is the minimum number of workstations needed if the maximum output rate is to be sought?
- What cycle time will provide an output rate of 125 units per day?
- What output potential will result if the cycle time is (1) 9 minutes? (2) 15 minutes.
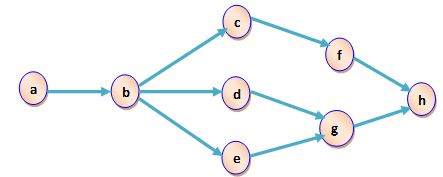
Q2. A manager wants to assign tasks to workstations as efficiently as possible, and achieve an hourly output of 33.5 units. Assume the shop works a 60-minute hour. Assign the tasks shown in the accompanying precedence diagram (times are in minutes) to workstations using the following rules:
a. In order of the most following tasks.
b. In order of the greatest positional weight.
c. What is the efficiency?
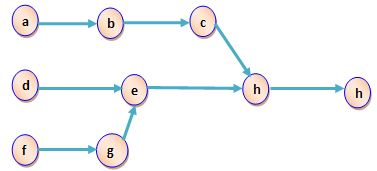
Q3. A manager wants to assign tasks to workstations as efficiently as possible, and achieve an hourly output of 4 units. The department uses a working time of 56 minutes per hour. Assign the tasks shown in the accompanying precedence diagram (times are in minutes) to workstations using the following rules.
a. In order of most following tasks. Tiebreaker: greatest positional weight.
b. In order of greatest positional weight.
c. What is the efficiency?
Task time information table:
|
Task
|
Task time in minutes
|
|
A
|
3
|
|
B
|
2
|
|
C
|
4
|
|
D
|
7
|
|
E
|
4
|
|
F
|
5
|
|
G
|
6
|
|
H
|
9
|
|
I
|
5
|
4. A producer of inkjet copiers is planning to add a new line of copiers, and you have been asked to balance the process, given the following task times and precedence relationships.
a. Assume that cycle time is to be the minimum possible.
i. Do each of the following:
ii. Draw the precedence diagram.
iii. Assign tasks to stations in order of greatest number of following tasks.
iv. Determine the percentage of idle time.
v. Compute the rate of output in copiers per day that could be expected for this line assuming a 420 minute working day.
b. Answer these questions:
i. What is the shortest cycle time that will permit use of only two workstations? Is this cycle time feasible: identify the tasks you would assign to each station?
ii. Determine the percentage of idle time that would result if two stations were used.
iii. What is the daily output under this arrangement?
iv. Determine the output rate that would be associated with the maximum cycle time.
|
Task
|
Length (in minutes)
|
Immediate Follower
|
|
A
|
0.2
|
b
|
|
B
|
0.4
|
d
|
|
C
|
0.3
|
d
|
|
D
|
1.3
|
g
|
|
E
|
0.1
|
F
|
|
F
|
0.8
|
g
|
|
G
|
0.3
|
h
|
|
H
|
1.2
|
end
|
Q5. As part of a major plant renovation project, the industrial engineering department has been asked to balance a revised assembly operation to achieve an output of 20 units per eight-hour day. Task times and precedence relationships are as follows:
|
Task
|
Duration (in minutes)
|
Precedence Task
|
|
A
|
0.2
|
b
|
|
B
|
0.4
|
C
|
|
C
|
0.2
|
f
|
|
D
|
0.4
|
e
|
|
E
|
1.2
|
g
|
|
F
|
1.2
|
g
|
|
G
|
1.0
|
end
|
Do each of the following:
a. Draw the precedence diagram.
b. Determine the minimum cycle time, the maximum cycle time, and the calculated cycle time.
c. Determine the minimum number of workstations needed.
d. Assign tasks to workstations on the basis of greatest number of following tasks. Use longest processing time as a tiebreaker. If ties still exist, assume indifference in choice.
e. Compute the percentage of idle time for the assignment in part d.
Q6. Using the following factor ratings, determine which location alternative should be chosen on the basis of maximum composite score, A, B, or C.
|
Factor
|
weight in percent
|
Location rated between 0 and 100
|
|
A
|
|
B
|
C
|
|
Convenience
|
15
|
80
|
|
70
|
60
|
|
Parking facilities
|
20
|
72
|
|
76
|
92
|
|
Display area
|
18
|
88
|
|
90
|
90
|
|
Shopper traffic
|
27
|
94
|
|
86
|
80
|
|
Operating costs
|
10
|
98
|
|
90
|
82
|
|
Neighborhood
|
10
|
96
|
|
85
|
75
|
| |
100
|
|
|
|
|
Q7. A manager has recovered an analysis of several cities being considered for a new office complex. The data (10 points maximum) are
|
Factor
|
Location
|
|
A
|
B
|
C
|
|
Business services
|
9
|
5
|
5
|
|
Community services
|
7
|
6
|
7
|
|
Real state cost
|
3
|
8
|
7
|
|
Construction costs
|
5
|
6
|
5
|
|
Cost of living
|
4
|
7
|
8
|
|
Taxes
|
5
|
5
|
4
|
|
Transportation
|
6
|
7
|
8
|
- If the manager weighs the factors equally, how would the locations stuck up?
- If business service and construction cost are given weights that are double the weights of other factors, how would the locations stack up?
Q8. A toy manufacturer produces toys in five locations throughout the country. Raw materials (primary barrels of powdered plastic) will be shipped from a new, centralized warehouse whose location is to be determined. The monthly quantities to be shipped to each location are the same. A coordinate system has established, and the coordinates of each location have been determined as shown. Determine the coordinates of the centralized warehouse.
|
Location
|
X, Y
|
|
A
|
3, 7
|
|
B
|
8, 2
|
|
C
|
4, 6
|
|
D
|
4, 1
|
|
E
|
6, 4
|
Q9. A company makes products from rough tree fibers. Its product line consists of five items processed through one of five machines. The machines are not identical, and some products are better suited to some machines. Given the following production time in minutes per unit, determine an optimal assignment of product to machine.
|
Product
|
Machine
|
|
A
|
B
|
C
|
D
|
E
|
|
1
|
17
|
10
|
15
|
16
|
20
|
|
2
|
12
|
9
|
16
|
9
|
14
|
|
3
|
11
|
16
|
14
|
15
|
12
|
|
4
|
14
|
10
|
10
|
18
|
17
|
|
5
|
13
|
12
|
9
|
15
|
11
|
Q10. Sunshine House, a supplier of Girl Scout cookies, has received a contract this year. Sunshine currently has five production lines, each of which will be dedicated to a particular kind of cookie. The production lines differ by sophistication of machines, site, and experience of personnel. Given the following estimates of processing times (in hours), assign cookies to line to minimize the sum of completion times:
|
Cookies
|
Production Line
|
|
1
|
2
|
3
|
4
|
5
|
|
Chocolate Mint
|
30
|
18
|
26
|
17
|
15
|
|
Peanut Butter
|
23
|
22
|
32
|
25
|
30
|
|
Shortbread
|
17
|
31
|
24
|
22
|
29
|
|
Fudge Delight
|
28
|
19
|
13
|
18
|
23
|
|
Macaroons
|
23
|
14
|
16
|
20
|
27
|
Q11. Today is day 4 of the planning cycle. Sequence the following jobs by FCFS, SPT, SLACK, and DDATE. Calculate the mean flow time and mean tardiness for each sequencing rule. Which rule would you recommend?
|
Job
|
Processing Time (in days)
|
Due Date
|
|
A
|
3
|
10
|
|
B
|
10
|
12
|
|
C
|
2
|
25
|
|
D
|
4
|
8
|
|
E
|
5
|
15
|
|
F
|
8
|
18
|
|
G
|
7
|
20
|
Q12. To improve the service quality, the owner of dry-cleaning business has the business objective of reducing the number of dry-cleaned items that are returned for rework per day. Records were kept for a four-week period (the store is open Monday through Saturday), with the results given in the following table.
|
Day
|
Items Returned for Rework
|
Day
|
Items Returned for Rework
|
|
1
|
4
|
13
|
5
|
|
2
|
6
|
14
|
8
|
|
3
|
3
|
15
|
3
|
|
4
|
7
|
16
|
4
|
|
5
|
6
|
17
|
10
|
|
6
|
8
|
18
|
9
|
|
7
|
6
|
19
|
6
|
|
8
|
4
|
20
|
5
|
|
9
|
8
|
21
|
8
|
|
10
|
6
|
22
|
6
|
|
11
|
5
|
23
|
7
|
|
12
|
12
|
24
|
9
|
a. Construct a c chart for the number of items per day that are returned for rework.
b. Do you think the process is in the state of control?
c. Should the owner of the dry-cleaning store take action to investigate why 12 items were returned for rework on day 12? Explain. Would your answer be changed if 20 items were returned for rework on day 12?
d. On the basis of the results in (a), what should the owner of the dry-cleaning store do to reduce the number of items per day that are returned for rework?
Q13. Twenty samples in each of which 200 items were taken by an operator at a workstation in a production process. The number of defective items in each sample was recorded as follows:
|
Sample
|
Number of Defectives
|
Sample
|
Number of Defectives
|
|
1
|
12
|
11
|
16
|
|
2
|
18
|
12
|
14
|
|
3
|
10
|
13
|
12
|
|
4
|
14
|
14
|
16
|
|
5
|
16
|
15
|
18
|
|
6
|
19
|
16
|
20
|
|
7
|
17
|
17
|
18
|
|
8
|
12
|
18
|
20
|
|
9
|
11
|
19
|
21
|
|
10
|
14
|
20
|
22
|
Management wants to develop an appropriate chart using 3-sigma limits. Set up the p-chart and plot the observations to determine if the process was out of control at any point.
Q14. A tire producing company, as part of its inspection process, tests its tires for tread wear under simulated road conditions. Twenty samples of three tires each were selected from different shifts over the last month of operation. The tread wear is reported below in hundredths of an inch.
|
Sample
|
Tread
Wear
|
Sample
|
Tread
Wear
|
|
1
|
44
|
41
|
19
|
11
|
11
|
33
|
34
|
|
2
|
39
|
31
|
21
|
12
|
51
|
34
|
39
|
|
3
|
38
|
16
|
25
|
13
|
30
|
16
|
30
|
|
4
|
20
|
33
|
26
|
14
|
22
|
21
|
35
|
|
5
|
34
|
33
|
36
|
15
|
11
|
28
|
38
|
|
6
|
28
|
23
|
39
|
16
|
49
|
25
|
36
|
|
7
|
40
|
15
|
34
|
17
|
20
|
31
|
33
|
|
8
|
36
|
36
|
34
|
18
|
26
|
18
|
36
|
|
9
|
32
|
29
|
30
|
19
|
26
|
47
|
26
|
|
10
|
29
|
38
|
34
|
20
|
34
|
29
|
32
|
a. Determine the control limits for the mean and range charts.
b. Plot the control limits for the mean outside diameter and the range.
c. Are there any points on the range chart that are out of control? Comment on the chart.
Provide complete and step by step solution for the question and show calculations and use formulas.