Assignment:
Problem 1.
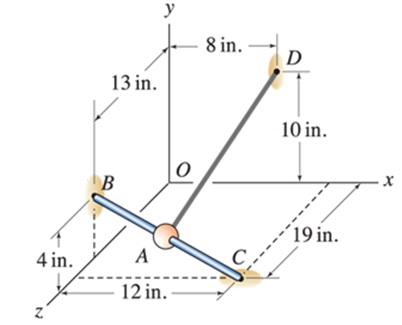
Bead A has negligible weight and slides without friction on rigid bed bar BC. An elastic cord AD, which supports a 10 lb tensile force, is attached to the bead. At the instant shown, the bead has zero velocity. For the position of the bead given below, determine the vector components of the cord tension that act para Ilel and perpendicular to direction BC of the bar (your answers should be vectors). Due to the cord tension, will the bead slide toward point B or C?
- Bead A is positioned halfway between points B and C.
- Bead A is 1/4 the distance from point B to point C.
Problems 2.
Components of a machine (not shown in the figure) are actuated by motion of a threaded collar C that slides on a fixed bar DEFGHI. Segment DE of the bar is straight and vertical, segment FGis straight where the coordinated of points F and G are given in the figure, and segment HI is straight and horizontal. The collar's motion is controlled by screw AB, which is turned by the motor at point A. If the force in the screw is 50 N1 compression, use the dot product to determine the component of the screw force in the direction of the bar for the positions of the collar given below. Also determine the component of the screw force perpendicular to the bar.
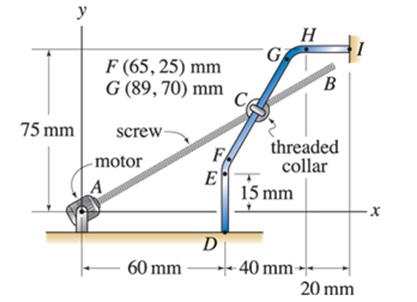
a. Collar C is 2 mm below point E.
b. Collar C is 1/3 the distance from point Fto point G.
Problem 3.
The gearshift lever AB for the transmission of a sports car has position vector r whose line of action passes through points A and B. The driver applies a force it to the knob of the lever to shift gears. If the component of f perpendicular to the gearshift lever must be 5 N to shift gears, determine the magnitude F of the force.
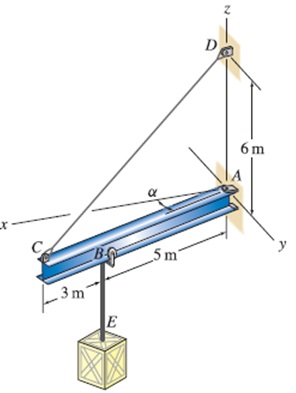
A wall-mounted jib crane consists of an I beam that is supported by a pin at point A and a cable at point C, where A and C lie in the xy plane. A crate at E is supported by a cable that is attached to a trolley at point B where the trolleymay move along the length of the I beam. The forces supported by cables CD and BE are 3 kN and 5 kN, respectively. For the value of a ngle a given below, determine expressions for the forces the two cables apply to the I beam.
a =0°.
a = 40°.
a =70°.
General values of a where -90°s a590°.
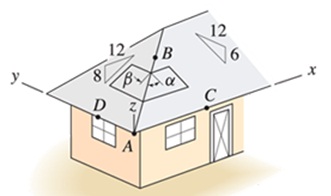
Problem 4.
An architect specifies the roof geometry shown for a building. Each of lines EAB, BD, DCG, EG, and AC are straight. Two forces of magnitude P and Qacting in the -y direction are applied at the positions shown.
Determine the components of the force P in directions normal and parallel to the roof at point A. Express your answer in terms of P.
Problem 5. The manufacturer of a welded steel bracket spe cifi es the working loads depicted in the figure of Pa versus Pt. Values of P„ and Pt that lie within the shaded region are allowable, while values that lie outside of the region are unsafe. Such a diagram is often called an interaction diagram because it characterizes the combined effect that multiple loads have on the strength of a component. For the loading and geometry shown, determine the range of values load P may have and still satisfythe manufacturer's combined loading criterion.
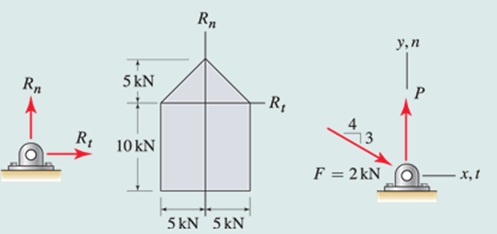
Problem 6.
For the loading and geometry shown, use the interaction diagram of Prob. 2.168 to determine if the manufacturer's combined loading criterion is satisfied.
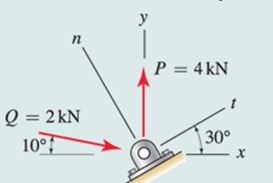
Problem 7.
Structure ARCO is rigid and is built-in at point A. Point A is at the origin of the coordinate system, points B and 0 have the coordinates B (16,24,48) in. and 0 (26 ,52 , -2) in., and point C is at the midpoint of the straight bar AB. Portion CD of the structure is perpendicular to bar AB.
a. Verifythat portion CD of the structure is indeed perpendicular to bar AB.
b. Determine the unit vector p that is perpendicular to both AB and CD such that this vector has a positive x component.
c. The force j; applied to point D of the structure has 600 lb magnitude and direction angles 8X = 108°, Oy = 36°, and Oz =60°. Determine the components of the 50 N force, namely PAB, Pw, and in the directions AB, CD, and p, respectively.
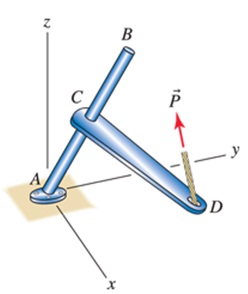
Problem 8.
A building's roof ha s'16 in 12" slope in the front and back and "8 in 12" slope on the sides. Determine the angles a and p that should be used for cutting sheets of plywood so they properly meet along edge AB of the roof. Hint: Write the position vector F48 (where B is some point along the edge of the root) two ways: 1.48 = ?AC + leg and 68 = /An + FOR. Then use the roof slopes to help write Fen and inn such that the magnitudes of the two expressions for ?AB are the same.
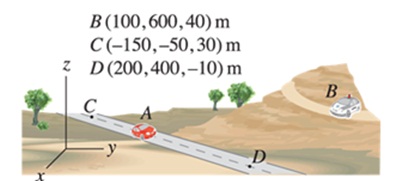
Problems 9.
A sports car at point A drives down a straight stretch of road CD. A police car at point B uses radar to measure the speed of the car, and obtains a reading of 80 knxh. For the position of the car given below, determine the speed of the car. Note that the 80 km,h speed measured by the radar gun is the rate of change of the distance betwe en the car and the radar gun.
- The car is 30% of the distance from point C to point D.
- The car is 60% of the distance from point C to point D.
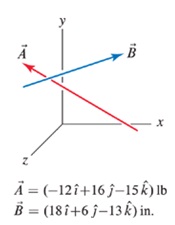
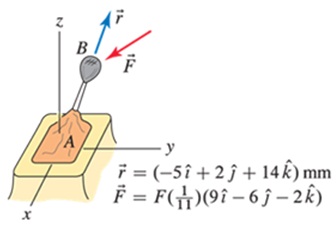
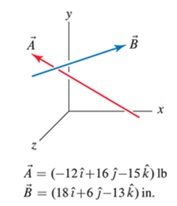
a. Evaluate „f
b. Evaluate
c. Comment on any differences between the resuks of Parts (a) and (b).
d. Use the dot product to show the resuk of Part (a) is orthogonal to vectors „i and R.
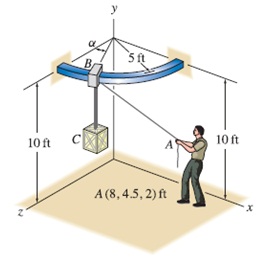
A crane consists of a quarter-circular bar that lies in a plane parallel to the xz plane with a low-friction collar
Problems 10.
A crane consists of a quarter-circular bar that lies in a plane parallel to the xz plane with a low-friction collar at point B that ma yshde on the bar. The forces supported by cables AB and BC are 30 lb and 1500 lb, respectively, and the coordinates of point A are given in the figure. For the value of angle a given below, determine expressions for the forces the two cables applyto the collar at point B.
a=0°.
a= Ir.
0=60°.
General values of awhere 0° s a s 90°.
a. Determine the angle between vectors ,f and n.
b. Determine the components of A parallel and perpendicular to A.
c. Determine the vector components of A paralel and perpendicular to A.