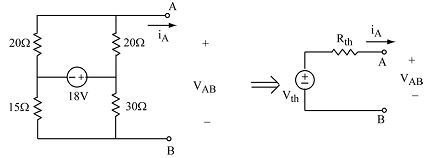
1. Determine the Thevenin equivalent of the network shown on the left.
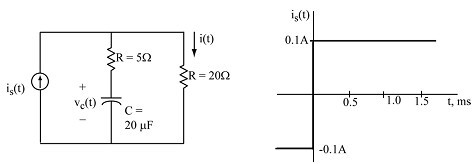
2. In the circuit shown, the source current is(t) is -0.1A prior to t = 0, and +0.1 A after t = 0, as shown in the plot. Determine the current i(t) for t > 0.
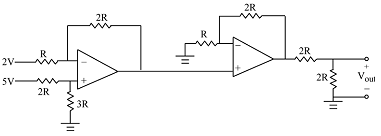
3. For the ideal op amp circuit shown, determine the voltage Vout.
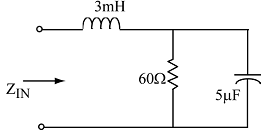
4. Determine ZIN of the network shown at a frequency ω = 104r/s.
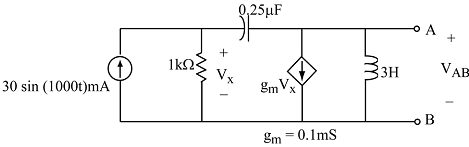
5. Using phasor representation for voltages, currents, and impedances, write two KCL equations that would allow us to solve for VX and VAB. (Do not solve for VX or VAB.) The terminals A & B are open circuited.
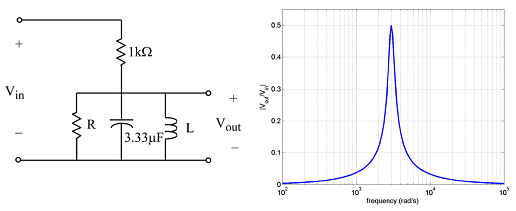
6. For the network shown we measure |Vout/Vin| as we vary the frequency ω of the sinusoidal voltage. A plot of |Vout/Vin| is shown. Determine R and L.
7. An ideal 400Veff ∠0° source at ω = 100 rad/s with a series impedance of Zs delivers power to a load of impedance ZL = (10 - 5j)?. The current I is (30 + 10j) Aeff.
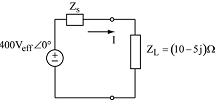
a) Find the series impedance Zs.
b) Determine the complex power generated by the (ideal) 400V source.
c) Determine the complex power absorbed by ZL.
d) Determine the power factor of the load ZL. (Remember to designate "leading" or "lagging"!)
e) What inductance or capacitance, when placed in parallel with the load, will increase its power factor to 1? (You may ignore the impedance Z for this problem.)
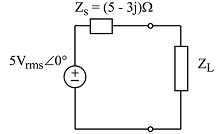
8. In the circuit shown, determine the value of load impedance ZL that will absorb the maximum average power from the source. Determine the maximum average power absorbed.
Attachment:- Assignment.rar