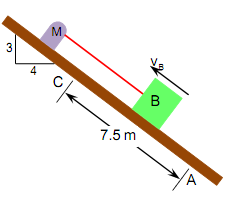
Problem 1. The motor pulls 15 kg Box B up the slope. The box passes point A with speed 10 m/s When it passes point C its speed has decreased to 5 m/s/ The rate of acceleration is constant. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the box and the plane is μs = 0.2. Determine the tension in the cable as the box moves between A and C.
Problem 2. The 80 lb Boy Scout stands on the blue bathroom scale in an elevator. Determine the reading on the scale's dial (or digital output, whatever) when t 3s if (a) the elevator moves upward with constant velocity v= 9 ft/s (b) the elevator moves upward with velocity
v = 1/3(t3) ft/s; and (c) the elevator moves upward with velocity v = (18 - 1/3 t3) ft/s.

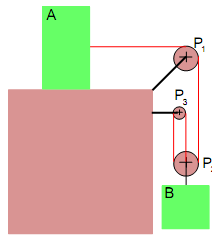
Problem 3. The continuous inextensible red cable connects blocks A and B. Block A weighs 16.1lb and block B weighs 12.0 lb. The coefficients of static and kinetic friction between block A and the odd colored surface are μs = 0.2 and μk = 0.1, respectively. The system is released from rest. Determine (a) the acceleration of each block, (b) the tension in the cable, (c) the speed of block B after block A has moved 2 ft, and (d) the speed of block A 2s after motion begins.
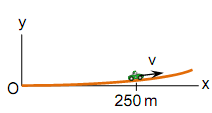
Problem 4. The 2.5Mg car moves along the path described by the equation y = (5*10-9)x4m. When the car is passes the point at which x = 250m, it moves with speed v = 120 km/hr which increases at 1.2 m/s2. Determine normal and tangential force components the road exerts on the car at this instant. Treat the car as a particle and neglect its dimensions (assume its mass center moves along the path.)
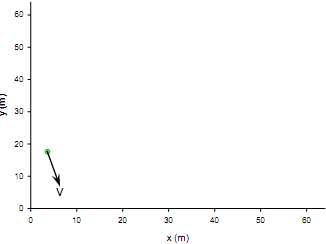
Problem 5. A 12 kg particle moves along the path defined by xy = 64 m2 with a constant speed v = 12 m/s. A particle moves along the path defined by xy 64 m2 with a constant speed v = 12 m/s. Determine the x and y force components the path must exert on the particle to keep it on the path when it passes x = 4m.