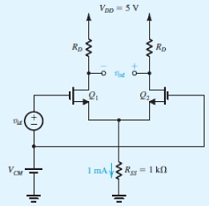
Response to the following problem:
The differential amplifier in Fig. utilizes a resistor RSS to establish a 1-mA dc bias current. Note that this amplifier uses a single 5-V supply and thus the dc common-mode voltage VCM cannot be zero. Transistors Q1:and Q2:have k1nW/L = 2.5 mA/V2, Vt =0.7 V, and λ = 0.
(a) Find the required value of VCM.
(b) Find the value of RD that results in a differential gain Ad of 8 V/V.
(c) Determine the dc voltage at the drains.
(d) Determine the single-ended-output common-mode gain ?VD1/?VCM. (Hint: You need to take 1/gm into account.)
(e) Use the common-mode gain found in (d) to determine the change in VCM that results in Q1:and Q2:entering the triode region.