Assignment Purpose: The purpose of this assignment is to motivate students to seek to understand the fundamental principles in the design and analysis of mobile cellular communications systems.
Assignment 1A:
QUESTION 1: Assume that you have been hired to design a mobile cellular network based on LTE-Advanced (aka LTE-A) to serve Melbourne CBD. You are expected to use CelPlanner software for your design and analysis. The system operates in the LTE FDD Band 14 [LTE band 17: 704 - 748 MHz (UL) and 758 - 803 MHz (DL)]. Use carrier bandwidth of 1.4 MHz. Your report should include the following.
1. Do some research and describe the effect of the topography and morphology of the coverage area.
2. State how LTE-A with above frequency band and bandwidth can be designed for Melbourne CBD using CelPlanner.
Your report should include images from CelPlanner screen and explanation of the various choices that you have made.
Assignment 1B:
QUESTION 2: The mobile user equipment (UE) and the evolved Node B (eNB) specified in Table 1 are used in LTE cellular network operating in a large city at 700MHz (i.e. LTE band 17: 704 - 748 MHz (UL) and 758 - 803 MHz (DL)]. Using the Hata's model, calculate the following:
a) The maximum cell radius for forward link (eNB-UE) and zero fade margin (i.e. RX threshold = - 110 dBm).
b) The maximum cell radius for the reverse link (UE-eNB) for a zero fade margin (i.e. RX threshold = -114 dBm).
c) Having calculated the forward and reverse links, is the link balanced? (Justify yes or no)
d) A fade margin must be allowed for proper operation of the cellular system. State the reason for that.
e) What is the maximum cell radius of the forward and reverse link if a fade margin of 8 dB is used?
|
eNB:
|
|
|
Frequency band
|
700 MHz
|
|
Transmitter power
|
55 Watts
|
|
Receiver threshold
|
-110 dBm
|
|
Antenna gain
|
12 dBd
|
|
Antenna height
|
60 m
|
|
Feeder loss (transmitter to antenna)
|
2 dB
|
|
UE:
|
|
|
Transmitter power
|
1 Watt -
|
|
Receiver threshold
|
114 dBm
|
|
Antenna gain
|
1 dBd
|
|
Antenna height
|
1.5 m
|
Table 1: The mobile user equipment (UE) and the evolved Node B (eNB) specification
QUESTION 3: Figure 1 shows a cellular mobile telecommunication network. The cell radius is 5km and the numbering of one cluster only is shown.
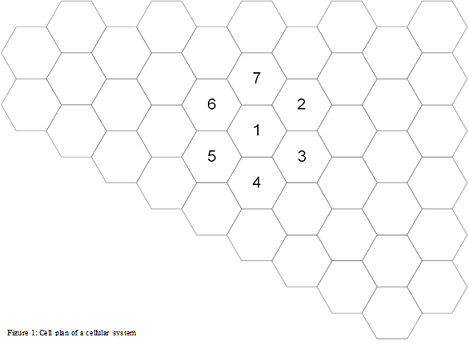
a) Number the remainder of the cell sites for this configuration to keep the co-channel interference to the barest minimum.
b) What is the frequency reuse distance for this configuration?
c) The eNB at a cell site can use either directional or omnidirectional antennas or both. Give reasons for the choice of any of antenna configuration. On what basis did you make your choice?
d) How would you increase the radio coverage of a cell? List and briefly explain three methods. Discuss the pros and cons of each choice.
e) If increasing the radio coverage of one cell resulted in an unacceptable level of co-channel interference. How would you go about reducing the interference to achieve an acceptable network operation?
Note - Need Assignment 1A only.
Take one step closer to Telecommunication Modelling and Simulation Assignment Help service and make your academic life successful!
Tags: Telecommunication Modelling and Simulation Assignment Help, Telecommunication Modelling and Simulation Homework Help, Telecommunication Modelling and Simulation Coursework, Telecommunication Modelling and Simulation Solved Assignments