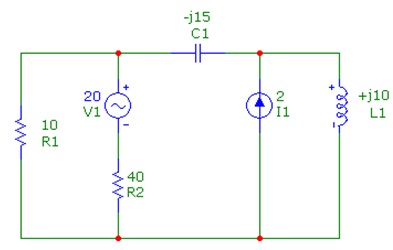
Question 1: Find out the current via each component, in polar form, by using mesh analysis. The source voltages are rms with an angle of 0 degrees.
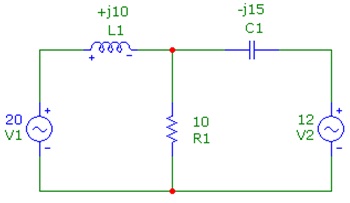
Question 2: Find out the current via each component, in polar form, by using mesh analysis. The source voltages are rms with an angle of 0 degrees.
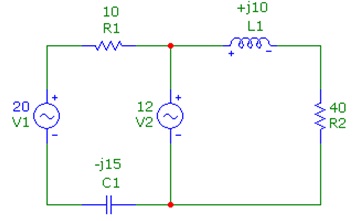
Question 3: Find out the voltage across each component, in polar form, by using nodal analysis. The source currents are rms with an angle of 0 degrees.
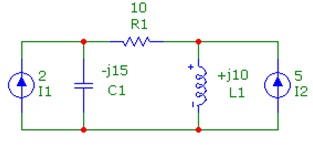
Question 4: Find out the voltage across each component, in polar form, by using nodal analysis. The source currents are rms with an angle of 0 degrees.
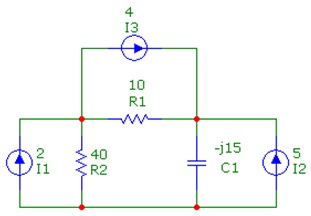
Question 5: Perform some type of source conversion and use mesh or nodal analysis to find out the current through R1 or the voltage across R1. The source values are rms at 0 degrees.