Question 1) For this problem, consider the following network topology:
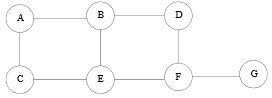
Assume that routers are running RIP, and are all turned on simultaneously. Recall that in RIP, weight assigned to each link is one. You can also suppose that if RIP identifies multiple paths of equal cost, it selects one randomly.
The initial routing table at node A is:
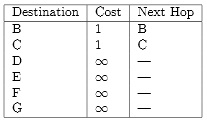
Fill in the following tables to demonstrate the initial routing table at node F:
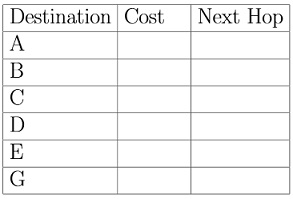
Question 2) Now demonstrate the contents of the routing table after each iteration of the algorithm:
(a) After iteration 1:

(b) After iteration 2:

Question 3) In some failure situations, administrator notices that it takes the exceptionally long time for the routing protocol to stabilize in this network.
(a) What problem with RIP is the cause?
(b) The administrator is told that BGP does not suffer from this problem. What prevents BGP from having this problem?