Assignment:
1. Consider the cost curves for a price-taking firm in the following figure:
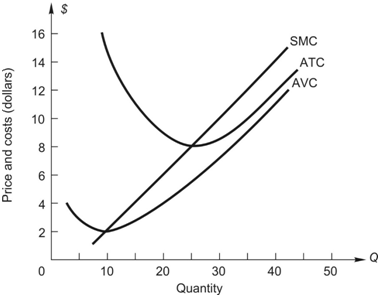
a. When price is $12 per unit of output, the firm maximizes profit by producing __________ units.
b. Since average total cost = $___________ for this output, total cost is $____________.
c. The firm makes an economic profit (loss) of $____________________.
d. Price falls to $8. The firm now maximizes profit by producing ______ units.
e. At this output level, total revenue = $__________ and total cost = $____________. Therefore the firm earns a profit (loss) of $____________.
f. Price falls to $6. The firm now maximizes profit by producing _____________ units.
g. At this output level, average total cost is $_________ and total cost is $_____________. Total revenue = $____________ and the firm makes a loss of $________________.
h. Even though the firm makes a loss, it does not shut down because total variable cost is $____________, which leaves $_________ of total revenue to apply toward fixed costs.
i. If price falls below $_____________, the firm shuts down.
2. Consider a monopoly that faces the demand and cost curves in the figure below. The firm operates in the short run using a plant designed to produce 850 units optimally.
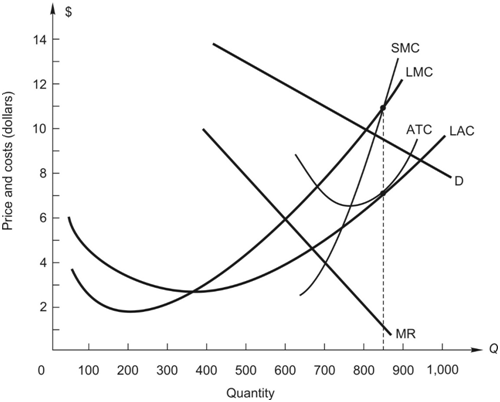
Please use SMC for Marginal cost curve. SMC represents short run marginal cost curve.
a. In the short run, the manager maximizes profit (or minimizes loss) by producing __________ units.
b. The monopolist charges $_________ per unit for its output.
c. Monopoly profit is $___________.