(a) Question 1. A. Using the concept of opportunity cost, explain the statement "There is no such thing as a free lunch".
(b) B Evaluate the statement 'The concept of opportunity cost is embedded in the demand curve'.
Question 2.In the study of Microeconomic, the question "How to produce" is one of the basic economic problems (BEPs). Using an example, discuss this concept. In your discussion, you must also discuss the rationale behind the principle of increasing cost.
Question 3. A. Explain why governments impose excise taxes on goods that are inelastic. Using cigarettes as an example, explain the impact of the government imposing a $1/packet tax on cigarettes. Use relevant diagram(s) to illustrate the effects of tax on this product.
(a) A fall in the price of beef from $30 to $20 has led to an increase on quantity demanded from 40,000 units to 60,000 units. Using the mid-point method, calculate the price elasticity demand for lamb and interpret the value obtained.
Question 4.
The table below shows the deman and supply for ipods at varying price per ipod:
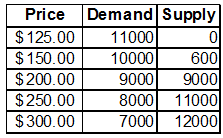
(a) In the graph provided, plot the supply and demand curves for ipods, and determine the equilibrium price and quantity.
(b) What effect will a decrease in the price of microchip (input) on the equilibrium price and quantity of ipods? What assumptions have you made to provide your answers?
(c) What effect will an increase in the price of a substitute on the equilibrium price and quantity of ipods? What assumptions have you made to provide your answers?
(d) If the price in the market was $250 per ipod, explain the process where equilibrium can be restored in the market.