Binary Choice:
Problem 1. Suppose that a small, closed economy opens its markets to trade. If the world price of good X is greater than the domestic price of good X we can predict that
a) This country will export good X to the world and domestic consumers will benefit from this additional trade.
b) This country will export good X to the world and domestic consumers will consume less good X.
Problem 2. People in the United States can get upset when the price of gasoline climbs above $4.00 per gallon and they can argue that the government ought to limit the price of gasoline. From your study of economics you know
a) That if the government imposes an effective price ceiling that this will lower the price of ga soline and create a situation of excess supply.
b) That if the government imposes an effective price ceiling that gasoline will need to be allocated to consumers by some other means than just price since this price ceiling will create a situation of excess demand.
Problem 3. In class, the joint PPF we constructed based on the production of two individuals had a kink point due to:
a) The individuals having different opportunity costs of production for the two goods.
b) The individuals having access to different levels of resources.
Problem 4. Argentina and Brazil produce only Mate (tea) and coffee. Brazil has comparative advantage over Argentina in produci ng coffee. Given that there is trade between the two countries, and that each country is producing both goods, we can co nclude that the production ________.
a) Is efficient.
b) Is not efficient
Problem 5. Investment spending is spending on productive physical capital. According to the national accounts system the construction of a new house
a) would be included as a part of inve stment spending.
b) would not be included as a part of investment spending.
Problem 6. Choose the true statement:
a) If nominal GDP in an economy is growing over time this implies that over time real GDP in this economy may be increasing, decreasing or remaining constant.
b) GDP per capita is a measure that can be used to assess how unequal the income distribution is.
Problem 7. Refer to the graph s below. Which move best illustrates a change in quantity demanded?
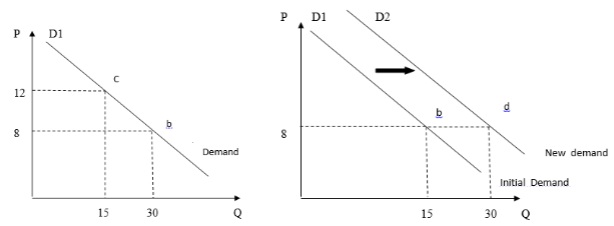
a) The move from b to c on the graph on the left side.
b) The move from b to d on the graph on the right side.
Problem 8. The price of tea , a substitute for coffee, increases. At the same time, robots are developed which prove to lower the cost of coffee production. In the market for coffee, we should expect to see curves shift. The supply curve of coffee will____ and the demand curve for coffee will ____.
a) shift to the right , shift to the left.
b) shift to the right , shift to the right
Problem 9. If in 2015 the unemployment rate is higher than in 2014 and the total population stays the same , fewer people have jobs.
a) This statement must be true.
b) This statement may not be true.
Problem 10 . “The federal government should increase taxes to offset the costs of the war.” This is an example of a _______ statement.
a) Positive
b) Normative
Multiple Choice:
Use the following information to answer the next two (2) questions. Consider the small, closed economy of Milta. In the market for oranges in Milta you know the following:
Domestic Demand for oranges: Q = 500 – 100P
Domestic Supply of oranges: Q = 50P – 100
Furthermore, you know that the world price of ora nges is $3.
Problem 11 . If this market opens to trade, then the quantity of oranges supplied domestically will
a) decrease by 50 units.
b) be larger than the quantity supplied by foreign producers.
c) be smaller than the quantity supplied by foreign producers.
d) Answers (a) and (b) are both correct.
e) Answers (a) and (c) are both correct.
Problem 12 . Suppose that Milta opens its orange market to trade while simultaneously imposing an import quota of 100 units of imported oranges. Given this information,
a) the price of oranges in Milt a will be less than $4 and this policy will increase consumer surplus relative to the orange market being a closed market.
b) the price of oranges in Milta will be greater than $3 and this policy will decrease producer surplus relative to the orange market be ing an open economy.
c) consumers in Milta will be better off than if this market were simply opened to trade while orange producers in Milta will be worse off than if this market were simply opened to trade.
d) the import quota will create a deadweight loss as the more cost efficient producers of oranges produce even more oranges.
e) we know with certainty that domestic consumers and domestic producers must be worse off since government implemented programs are always inefficient and harmful to everyone.
Use the following information to answer the next three (3) questions. Jacky and Dona each have linear PPFs in the production of good X and good Y. Each day Jacky can produce 4 units of X and 4 units of Y or, alternatively, he can produce 2 units of X and 5 units of Y. In any two - day period Dona can produce 4 units of X or, alternatively, 12 units of Y.
Problem 13 . Given that Jacky and Dona work 4 days a week, what is the maximum number of units of good X Jacky can produce in one week?
a) 16 units of good X
b) 48 units of good X
c) 24 units of good X
d) 12 units of good X
Problem 14. Given the above information, which of the following statements is true?
a) Jacky has comparative advantage in producing Y.
b) Jacky and Dona can produce together at least 52 units of Y a week.
c) The point (X, Y) = (8, 44) is efficient.
d) In one week Jacky can produce more units of Y than can Dona.
e) Answers (a), (b), (c) and (d) are all not true.
Problem 15. Given that there is trade between Jacky and Dona, what is the acceptable range of prices in terms of good X for 2 units of good Y?
a) Between 1/3 unit of X and 2 units of X
b) Between ½ unit of X and 3 units of X
c) Between 2/3 unit of X and 4 units of X
d) Between 2/3 unit of X and 1 unit of X
e) Between 1/3 unit of X and 1/2 unit of X
Problem 16. Refer to the graphs below showing the supply of automobiles. Which of the graphs would best describe the impact of an increase in the wages and input prices firms must pay in order to produce automobiles?
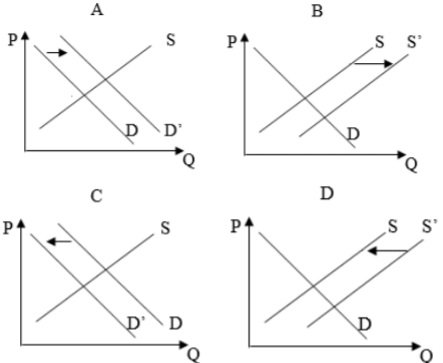
a) A
b) B
c) C
d) D
Problem 17 . The difference in the definition between Real and Nominal GDP is:
a) that Real GDP is measured by excluding some of the sectors.
b) that Real GDP is always smaller than Nominal GDP.
c) that the price level is changed from the base year to the current year.
d) Answers (a), (b), and (c) are all true statements when describing the difference between Real GDP and Nominal GDP.
e) Answers (a), (b) and (c) are all false statements when describing the difference between Real GDP and Nominal GDP
Problem 18. In a typical open economy GDP equals
a) C+I+G
b) C+I
c) C+I+X - M
d) C+G
e) None of the above
Problem 19. Consider the hypothetical economy consisting of three firms in the table below. In this economy, Steel, Inc buys intermediate goods from Ore, Inc. Motors, Inc buys its intermediate goods from Steel, Inc. C hoose the true statement from the following choices
Ore, Inc. Steel, Inc Motors, Inc.
Intermediate goods 0 4,200 9,000
Wages 2,000 3,700 10,000
Interest payments 1,000 600 1,000
Rent 200 300 500
Profit 1,000 200 1,000
Value of Sales 4,200 9,000 21,500
a) The total payments to factors are equal to the total value added. So the GDP in this economy is $ 21,500.
b) Summing the total value of sales of each of the three companies we can compute the GDP of this economy, which equals $34,700.
c) The value added by the firm Motors, Inc. is $12,500
d) Alternatives a) and b) are correct.
e) Alternatives a) and c) are correct.
Problem 20. Jeanne is preparing a report that will contrast the economies of China and the U.S. She would like to provide some measure that gives a “snapshot” picture of the standard of living for the two countries. Which of these choices would you encourage her to use?
a) Jeanne should use real GDP for the two countries since real GDP measures what is happening to the level of production in an economy over time using constant dollars.
b) Jeanne should use nominal GDP for the two countries since nominal GDP measures what is happening to the level of production in an economy over time using current dollars.
c) Jeanne should report just the median income for each economy measured in constant do llars since this will provide a measure of what the individual or family in the middle of the income distribution earns each year.
d) Jeanne should use the real GDP per capita for each country as her measure: although not perfect it provides a sense of what t he level of economic production per person is for each country.
e) Jeanne should describe the size of the agricultural sector in China and the U.S . Agricultural workers are always poorer than non - agricultural workers. Since China has more agricultural workers , the country is poorer
Problem 21. Consider the markets for butter and milk. Assume that milk is the only input used in the production of butter. Suppose that doctors successfully alter people’s tastes and preferences with regard to eating butter after a repeated campaign informing people of the dangers of consuming trans - fats that are contained in margarine (a non - dairy substitute for butter). Simultaneously, the number of milk farmers increases. Holding everything other than the butter and milk markets constant , which of the following statements is true?
a) The equilibrium quantity in the butter market will de crease while the equilibrium price of butter will be indeterminate.
b) The equilibrium quantity in the milk market will increase while the equilibrium price of milk will be indeterminate.
c) The equilibrium quantity in the butter market will be indeterminate while the equilibrium price of butter will increase.
d) The equilibrium quantity in the milk market will be indeterminate while the equilibrium price of milk will increase.
e) There will be an indeterminate outcome in both the butter and milk markets due to these changes.
Problem 22 . Suppose there are three groups of consumer s for Macbooks with the following demand curves, respectively:
Consumer Group 1’s Demand: P = 10 – Q1
Consumer Group 2’s Demand: P = 20 – Q2
Consumer Group 3’s Demand: P = 8 – Q3
Given the market supply is P = Q – 3, what is the equilibrium price and quantity in the market for MacBooks?
a ) P = 9 and Q = 12
b ) P = 10 and Q = 7
c ) P = 11 and Q = 5
d ) P = 8 and Q = 15
Problem 23. Frictional unemployment in an economy is 4 percent, cyclical unemployment is 3 percent, structural unemployment is 2 percent, and seasonal unemployment is 1 p ercent. Given this information what is the natural rate of unemployment for this economy?
a) 9
b) 6
c) 7
d) 5
Problem 24 . Joey is doing a report on unemployment and he has gathered the following data:
• Mike is 29 and a full - time father
• Cindy is 32 and a full - time student
• Lee is 40 and currently working 20 hours a week but is wantin g to work full - time
• Minzie is 54 and currently working at a full - time job but would like to work part - time
• Amy is 15 and works as a waitress at a local restaurant five days a week
• Moheeb is 50 and works full - time running his own business
• Jimmy is out of wo rk right now, is ready to work, and has been applying for a job regularly
• Mary is out of work right now, is applying regularly for jobs, but plans to travel overseas for the next two months
• Kevin is working full - time as a mechanic but wants to find a job t hat uses his engineering skills
• Marty is on vacation for the next three weeks from her job as an accountant Given this information, which of the following statements are true?
a) The labor force in Joey’s data would have a value of 10; the number of unemployed would equal 2; and the number of employed would equal 5.
b) The labor force in Joey’s data would have a value of 6; the number of unemployed would equal 2; and the number of employed would equal 5.
c) The labor force in Joey’s data would have a value of 5; the number of unemployed would equal 1; and the number of employed would equal 4.
d) The labor force in Joey’s data would have a value of 8; the number of unemployed would equal 3; and the number of employed would equal 5.
e) The labor force in Joey’s data would have a value of 6; the number of unemployed would equal 1; and the number of employed would equal 5.
Problem 25 . Teddy’s Creations (located in Duluth, MN, USA) manufactures bathmats that they sell for $20 each on the web. In 2013 Teddy’s Creations manufactured 1,000 of these bathmats and sold 600 of them. Teddy, the owner of Teddy’s Creations during 2013 also purchased a number of items to use at home: he bought $400 worth of Italian shoes, $300 worth of California wine, and $250 worth of Wiscon sin cheese. In 2014 Teddy bought the same dollar value of Italian shoes, the same dollar value of California wine, but decreased his purchases of Wisconsin cheese by $100. In 2014 Teddy’s Creations produced 1,000 bathmats and sold 1200 bathmats at a price of $20 per bathmat. Given this information, which of the following statements is true about Teddy and Teddy’s Creations contribution to GDP?
a) The effect of these activities on GDP in 2013 is to increase GDP by $ 20,550 while the effect of these activitie s on GDP in 2014 is an increase of $ 20, 450.
b) The effect of these activities on GDP in 2013 is to increase GDP by $20,150 while the effect of these activities on GDP in 2014 is an increase of $24,050.
c) The effect of these activities on GDP in 2013 is to increase GDP by $20,950 while the effect of these activities on GDP in 2014 is an increase of $24,850.
d) The effect of these activities on GDP in 2013 is to increase GDP by $12,950 while the effect of these activities on GDP in 2014 is an increase of $24 ,450.
e) The effect of these activities on GDP in 2013 is to increase GDP by $12, 950 while the effect of these activities on GDP in 2014 is an increase of $24,850.