I. BINARY CHOICE QUESTIONS
1. The supply curve for bananas is represented by the equation Q = -3+P. Suppose that banana farmers in this market invent a new technology to grow bananas, so they can now produce more bananas at every price than they could before the invention of this new technology. Holding everything else constant, which of the following equations could represent this change in the supply curve?
a.) Q = -4+P
b.) Q = -2+P
2. A rightward shift of the demand curve means a decrease in demand.
a.) True
b.) False
3. Economic growth means a/an _______________ of the economy's production possibilities.
a.) Expansion
b.) Contraction
4. Let us analyze two countries, Venezuela and Ecuador. Assume that both countries produce two goods, hats and mittens. If Venezuela has an absolute advantage in producing both hats and mittens, there is never any gain from trade between these two countries no matter what the price range is between the two goods.
a.) True
b.) False
5. Determine whether the following statement is true.
"The fierce competition in today's highly competitive world economy poses great challenges for our country. Thus, if the US does not improve its productivity in every industry, it will soon have no comparative advantage in anything."
a.) True
b.) False
6. Assume there are only two goods, good X and good Y. If the Production Possibility Frontier for these two goods is bowed outward, then the opportunity cost of making one more unit of good X decreases as the amount of good X increases.
a.) True
b.) False
7. Jonathan can spend his time reading his economics textbook or reading his Sports Illustrated magazine. In twenty minutes, Jonathan can either read 7 pages of his economics text or 10 pages of his Sports Illustrated magazine. Today, Jonathan has 1 hour to dedicate to reading, and he would like to read 6 pages from his economic text and 20 pages from his Sports Illustrated magazine. This combination is ___________.
a.) Feasible
b.) Not feasible
8. Scott and Joe produce two goods: soft pretzels and beer. Both Scott and Joe have linear PPFs. Scott can produce 24 soft pretzels or 16 bottles of beer in one hour. Joe is able to produce 32 soft pretzels or 16 bottles of beer in two hours. Trade _______ occur if prices are set such that 13 bottles of beer are exchanged for every 8 soft pretzels.
a.) will
b.) will not
Use the information below to answer the next question.
Suppose we have a small closed economy described by the following domestic supply and domestic demand curves:
Domestic Supply: Qs = 5
Domestic Demand: Qd = 20 - P
Determine if the following statement is true or false.
9. "In this economy shifts in the demand curve, holding everything else constant, affect the equilibrium price and the equilibrium quantity."
a.) True
b.) False
10. Indeterminacy in prices happens when
a.) Supply and Demand move in the same direction.
b.) Supply and Demand move in opposite directions.
11. The effect of the introduction of a quota in a market is different from the effect of the introduction of a tariff in the market because
a.) the change in consumer surplus is greater under the quota than under the tariff.
b.) under a tariff the government receives revenue while under a quota the government does not receive revenue.
12. Suppose that the world price for a good is above the domestic price for that good. Assuming that the groups maximize their own surplus (producer or consumer surplus), which group would be in favor of government-imposed export restrictions?
a.) Producers.
b.) Consumers.
II. MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Use the information below to answer the next three questions.
Two students, Anja and Marianne are planning a bake sale. The two girls each know how to bake two desserts: apple strudel and chocolate chip cookies. Their production possibility frontiers for one day of baking are shown below. Assume that both PPFs are linear.
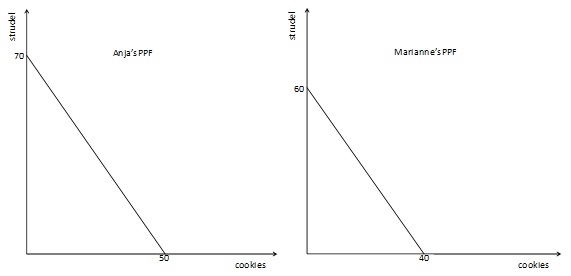
13. Which of the following combinations (cookies, strudels) is a feasible and efficient production plan for Marianne?
a.) (10, 20)
b.) (30, 16)
c.) (12, 42)
d.) (40, 10)
14. Anja's opportunity cost of producing an apple strudel (in terms of cookies) is:
a.) 6/4 cookies
b.) 5/7 cookies
c.) 2/3 cookies
d.) 7/5 cookies
15. If Marianne and Anja were to cooperate, which of the following would be an efficient distribution of production (ie: which dessert(s) should each girl bake)?
a.) Marianne should specialize in baking strudels, and Anja should bake both strudels and cookies.
b.) Marianne should specialize in baking cookies, and Anja should specialize in baking strudels.
c.) Anja should specialize in baking strudels, and Marianne should bake both cookies and strudels.
d.) Anja should specialize in baking cookies, and Marianne should specialize in baking strudel.
Use the information below to answer the next two questions.
Jessica and Nate produce two goods: X and Y. Both Jessica and Nate have linear PPFs. Nate has the comparative advantage in the production of good X and his PPF is shown below.
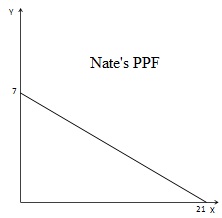
16. Based on this information, which of the following is a possible equation for Jessica's PPF?
a.) 4Y = 28 + X
b.) 4Y = 24 - 2X
c.) 6Y = 24 + 4X
d.) 5Y = 20 - X
17. In his garden Nick produces two vegetables: onions and green peppers. If he decides to grow only onions, Nick will be able to produce 24 onions. Nick faces a constant opportunity cost of 3 green peppers for each onion he grows. Which of the following is a feasible and efficient combination of onions and green peppers for Nick to grow?
a.) 21 onions and 10 peppers
b.) 22 onions and 9 peppers
c.) 20 onions and 12 peppers
d.) 21 onions and 3 peppers
Use the information below to answer the next two questions.
Suppose the following equations described the domestic supply and domestic demand curves for a good in a small closed economy.
Domestic Supply: Qs = 5
Domestic Demand: Qd = 20 - P
18. Given the above information which of the following statements is true?
a.) The consumer surplus in this market is equal to $25.
b.) The producer surplus in this market is equal to $37.5.
c.) The indeterminacy principle is not satisfied in this market because supply is not a function of price.
d.) Producer surplus equals producer revenue in this market because the price of the good does not depend upon the cost of production of this good.
19. Suppose the market described by the above equations is opened to trade with the rest of the world. Furthermore, suppose that the price of the good in the world market is $10. Holding everything else constant, this decision causes
a.) Consumer surplus in this economy to increase from $25 to $100.
b.) Producer surplus in this economy to decrease from $37.5 to $25.
c.) Producer surplus in this economy is not affected by the decision to open to trade.
d.) This economy to experience gains from trade equal to $12.5.
Use this information to answer the next two questions.
Suppose a market for a good in a small open economy is described by the following domestic supply and domestic demand curves:
Domestic Supply Curve: P = 10 + Qs
Domestic Demand Curve: Qd = 40 - P
The world price for this good is $10.
20. Suppose this market is opened to trade. Which of the following statements is true?
a.) Consumer Surplus = $450 and Gains from Trade = $225
b.) Consumer Surplus = $900 and Gains from Trade = $450
c.) Consumer Surplus = $225 and Gains from Trade = $450
d.) Consumer Surplus = $450 and Gains from Trade = $900
21. Suppose now that the government wants to tax the extra income from the gains from trade and redistribute the revenue. The government recognizes that taxing people has a cost. Determine which of the following statements is true.
a.) The most efficient proposal is for the government to tax the producers in this economy and redistribute the income from this taxation policy to the consumers.
b.) The income from redistribution should come from a positive tax on the gains producers and consumers receive from trade, and then the tax revenue should be redistributed equally among the producers and consumers.
c.) Income for redistribution should come from producer revenue as long as the costs of taxation do not exceed the gains from trade.
d.) Income for redistribution should come from consumer surplus as long as the costs of taxation do not exceed the gains from trade.
For the next two questions consider the production possibility frontier for Madland.depicted below.
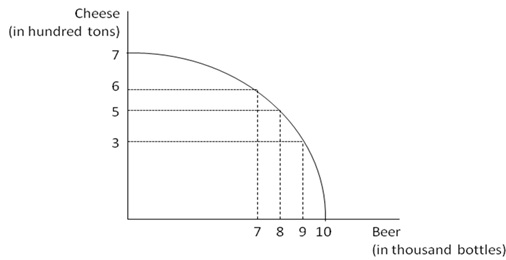
22. Suppose that the economy of Madland produces seven thousand bottles of beer and six hundred tons of cheese per year. To produce two thousand more bottles of beer per year, Madland will give up producing ______ hundred tons of cheese.
a.) 1
b.) 2
c.) 3
d.) 4
23. Now assume that Madland's economy produces nine thousand bottles of beer and three hundred tons of cheese per year. What is the opportunity cost of producing an additional two hundred tons of cheese in terms of beer?
a.) 1000 bottles
b.) 2000 bottles
c.) 3000 bottles
d.) 7000 bottles
Use the information below to answer the next two questions.
Assume that both the Earth Republic and the Mars Republic are closed economies with linear Production Possibility Frontiers. These PPFs are drawn in the graphs below. Currently the Earth Republic produces 7 billion bottles of clean water and 14 million tons of steel and the Mars Republic produces 2 billion bottles of clean water and 14 million tons of steel.
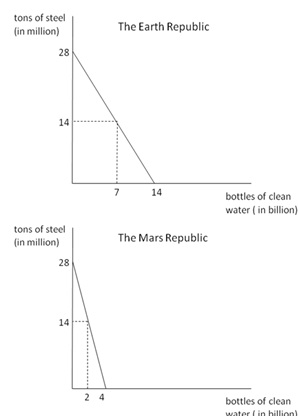
24. The opportunity cost of producing a billion bottles of clean water in the Earth Republic is _____ million tons of steel, while the opportunity cost of producing a million tons of steel in the Mars Republic is _____ billion bottles of water.
a.) 1/2; 1/7
b.) 1/2; 7
c.) 2; 7
d.) 2; 1/7
25. The _____ Republic has a comparative advantage in producing steel and the _____ Republic has an absolute advantage in producing clean water.
a.) Mars; Mars
b.) Mars; Earth
c.) Earth; Mars
d.) Earth; Earth
26. The effect of the introduction of an effective quota in a small open economy will be
a.) a reduction in consumer surplus with the government collecting no revenue.
b.) an increase in consumer surplus.
c.) an increase in government revenues arising from the quota.
d.)an increase in the surplus of the economy as a whole.
Use the information below to answer the next question.
In the US housing market, demand and supply are given as follows for the year 2009.
Qd = 11 - P
Qs = P - 2
27. A collapse in housing demand shifts the demand curve so that at every price one less unit of housing is demanded. At the same time, new houses are built such that 2 additional units of housing are available at every price. Determine the equilibrium price, P*, and the equilibrium quantity, Q*, after these demand and supply-side shocks.
a.) P* = 5 ; Q* =5.
b.) P* = 4 ; Q* = 6.
c.) Because both the demand and supply are shifting the effect on equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity is indeterminate.
d.) P* = 6 ; Q* = 8.