Question 1:
1.1 Sit Tight Limited, a company that manufactures chairs, is considering the purchase of a machine for R65 000.
The expected cash inflows generated by the machine are as follows:
Year Cash flow (R)
1 13 000
2 18 000
3 19 000
4 14 000
5 9 000
After the 5-year period the machine is expected to have a scrap value of R5 000. The company’s required rate of return is 7%.
Required:
Advise Sit Tight Limited on whether or not it should purchase the machine.
Base your recommendation on the net present value (NPV) of the investment.
1.2 R14 000 is invested in retail bonds at 15% per annum compound interest for 5 years. Calculate the value of the investment at the end of year 5.
1.3 Calculate the present value of R450 000 over 3 years, assuming a discount rate of 12%.
1.4 If you save R5 000 each year for the next 13 years in a savings account that pays 11% interest per annum, how much would you have saved?
1.5 Calculate the present value of R22 000 received annually at the end of every year for 8 successive years using a discount rate of 13%.
Question 2:
2.1 Jersey Limited is a manufacturer of milk bottles. The following information is obtained from their records.
Annual sales amount to 500 000 units. The purchasing price per unit is R3.
The carrying cost of inventory is equal to 20% of the purchase price of goods.
The ordering cost is R100 per order. Four days are required for delivery.
The desired safety stock for the firm is 4 000 units.
Required:
Calculate the economic order quantity (EOQ) for Jersey Limited.
2.2 Determine the re-order point for Jersey Limited. Assume a 360-day year.
Question 3:
Sun Manufacturing Limited produces light bulbs. The firm’s variable costs per light bulb amount to R4 and total fixed costs for the firm are R1 600 000. Sales of R6 000 000 are expected for the current year. The selling price per bulb is R15.
Required:
3.1 Calculate the expected marginal income for the year.
3.2 What will be the breakeven point (in units) of Sun Manufacturing Limited for the year?
Question 4:
Use the following information to answer questions 4.1 to 4.8.
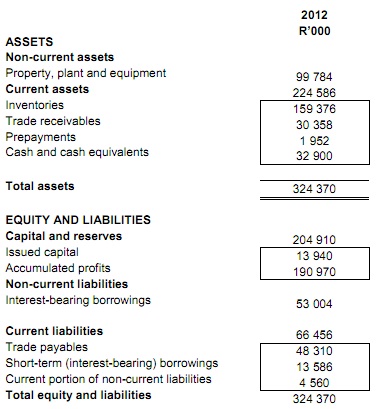
The balance sheet and income statement of Elephant Limited are as follows:
Balance sheet as at 31 December 2012:
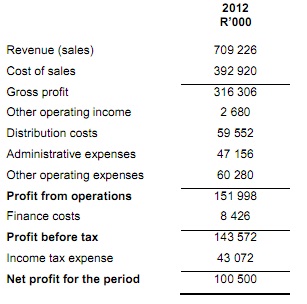
Income statement for the year ended 31 December 2012
Required:
Using the above information, calculate the following ratios for 2012:
Assume 365 days in a year throughout and round off to the nearest one decimal place.
4.1 Gross profit margin
4.2 Net profit margin
4.3 Return on assets before interest and tax
4.4 Return on equity
4.5 Current ratio
4.6 Quick ratio (acid test)
4.7 Debt ratio
4.8 Times interest earned ratio
Question 5: Seal Limited had sales of R100 000 in January, R80 000 in February and R90 000 in March.
The company forecasts sales for the coming months as follows:
April R110 000
May R100 000
June R120 000
Additional information:
The company had a cash balance of R20 000 on 1 April.
40% of the company’s sales is in cash.
Trade debtors (credit sales) are collected as follows:
20% during the month of sale
50 % during the first month following the sale
20% during the second month following the month of sale
10% during the third month following the month of sale
The company anticipates other cash income as follows:
April R10 000
May R12 000
June R11 000
Credit purchases for March amounted to R60 000.
The forecast for the next three months is as follows:
April R50 000
May R40 000
June R40 000
50% of credit purchases are paid in the month of purchase and the balance is paid the following month.
Rent paid amounts to R5 000 per month.
Salaries and wages amount to R20 000 per month.
An interest payment of R5 000 is due in May.
Equipment valued at R7 500 will be purchased in cash in April.
A trading fine of R10 000 is payable in June.
Required: Prepare the cash budget for Seal Limited for the months of April, May and June.