Assignment:
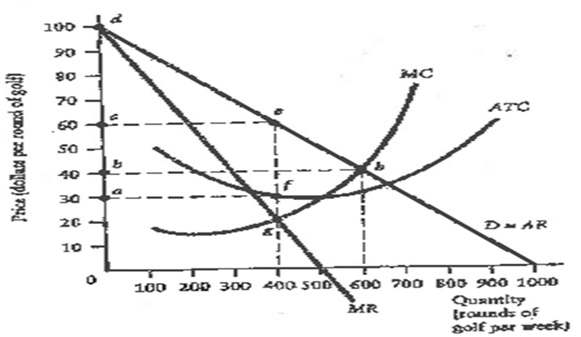
Question 1. The diagram below shows the demand, marginal revenue and cost curves for Jingyi who owns the only golf course in her community.
a. If Jingyi is a single-price monopolist, what is Jingyi's the profit maximizing quantity and price?
b. What is the average total cost at the profit maximizing level of output?
c. What is Jingyi's total weekly profit?
d. Calculate the deadweight loss to society.
e. If Jingyi was able to engage in Perfect price Discrimination, what price would she charge and how many rounds of gold would be sold each week?
f. What are the three conditions necessary for a firm to be able to price discriminate?
Question 2. The table below contains demand and production data for a profit maximizing monopolist.
a. Calculate total revenue, marginal revenue, marginal cost and profit.
b. What is the profit maximizing level of output and associated price?
c. What profit will receive at the profit-maximizing level of output?
d. Briefly explain what a monopolist does not have a supply curve.
|
Quantity (Q)
|
Price (P)
|
Total Revenue
|
Marginal Revenue
|
Total Cost
|
Marginal Cost
|
Profit
|
|
0
|
$35
|
$0
|
---
|
$0
|
---
|
|
|
100
|
32
|
|
|
4,800
|
|
|
|
200
|
29
|
|
|
6,000
|
|
|
|
300
|
26
|
|
|
7,000
|
|
|
|
400
|
23
|
|
|
8,400
|
|
|
|
500
|
20
|
|
|
10,000
|
|
|
|
600
|
17
|
|
|
11,700
|
|
|
|
700
|
14
|
|
|
13,500
|
|
|
Question 3. (Show all calculations)
Charlotte operates a yogurt stand in a perfectly competitive market on St. John's waterfront during the summer months. The market price for a yogurt is $2. The table below shows her hourly production function. The hourly wage rate is $12.
a. Complete the table below.
b. How many hours of labour will Charlotte hire?
c. Suppose Charlotte purchases new machinery which doubles labour productivity as shown in the fifth column in the table below. How many hours of labour will Charlotte now hire?
|
Labour
(L)
|
Total Product (Q)
|
Marginal Product of Labour
|
Marginal Revenue Product
|
Total Product (Q)
|
Marginal Product of Labour
|
Marginal Revenue Product
|
|
0
|
0
|
|
|
0
|
|
|
|
1
|
9
|
|
|
18
|
|
|
|
2
|
15
|
|
|
30
|
|
|
|
3
|
19
|
|
|
38
|
|
|
|
4
|
22
|
|
|
44
|
|
|
|
5
|
24
|
|
|
48
|
|
|
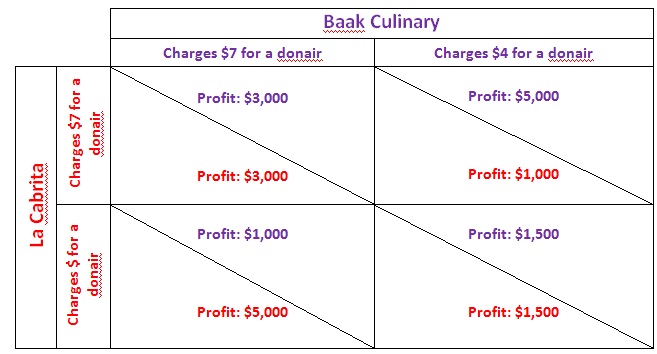
Question 4. Suppose Baak Culinary and La Cabrita are the only two firms operating in the late-night food market in Halifax. They can choose to cooperate and charge the same high price ($7) for their donairs or they can compete and charge a lower price ($4) - - - a lower price gains more market share. Below is the payoff matrix for this game.
a. Does either firm have a dominant strategy? Explain.
b. What is the best outcome if both firms collude?
c. Is there an incentive for either firm to cheat? Why?
d. In this game, what is the Nash equilibrium outcome? Explain.