I. Binary Choice Questions:
Question 1. Cnn.money.com wrote the following statement regarding the 2008 stimulus plan:“The package will pay individual taxpayers $600 and $1,200 for married taxpayers filing joint returns as long as they are below income caps of $75,000 for individuals and $150,000 for couples.” This statement is:
a. Positive
b. Normative
Question 2. Jeremy’s research interests include the behavior of GDP (Gross Domestic Product) of the United States and various European countries, unemployment, and the inflation rate. Jeremy’s interests belong to the field of:
a. Microeconomics
b. Macroeconomics
Question 3. In the line described by the equation y = -2x + 5, x and y are:
a. Positively related
b. Negatively related
Question 4. Suppose two countries engage in trade. To maximize total output, each country should produce the good for which it has:
a. Absolute advantage
b. Comparative advantage
Question 5. The graph below shows the Production Possibility Frontiers for Ann and Ben.
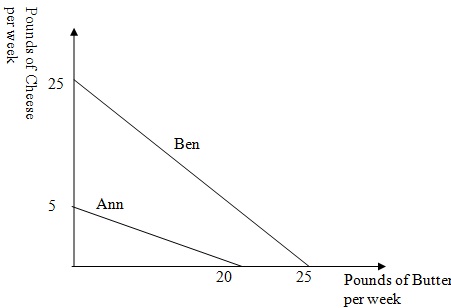
Who has the comparative advantage in producing cheese?
a. Ann
b. Ben
Question 6. Assume that Wisconsin and Illinois only produce and consume milk and corn, and that Wisconsin has absolute advantage in both milk and corn production. Can Wisconsin still benefit from trading with Illinois?
a. Yes
b. No
Question 7. Ramen noodles are an inferior good. Holding everything else constant, if people's income increases, then the price of ramen noodles will
a. Increase.
b. Decrease.
Question 8. Apple, the manufacturer of iPods, lowers the price of its product to attract new customers. Holding everything else constant, the change in the quantity demanded is a result of:
a. A shift to the right of the demand for iPods.
b. A movement along the demand curve.
Question 9. There was a severe drought in the areas where farmers grow potatoes. Meanwhile, the price of sweet potatoes decreased. Assume potatoes and sweet potatoes are substitutes in consumption. Given this information and holding everything else constant, what will happen to the equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity of potatoes?
a. The equilibrium quantity of potatoes will decrease, and the equilibrium price of potatoes will decrease.
b. The equilibrium quantity of potatoes will decrease, but the effect on the equilibrium price of potatoes is uncertain.
Question 10. A price ceiling is imposed by the government on the price of milk. This price ceiling is effective and results in an excess demand of 10 units of milk. If the demand for milk is given by the equation P = 60 – 4Q, and the supply of milk is given by the equation P = Q, then the price ceiling must be equal to
a. $20
b. $4
Use the following information for the next two (2) questions.
The supply of Packers’ football tickets is perfectly inelastic (that is, the market supply curve is a vertical line). The demand curve is downward sloping. Suppose Green Bay’s government decides to place an excise tax on tickets, and the GB Packers’ organization is legally responsible for paying the tax.
Question 11. The economic incidence of the tax will fall:
a. Solely on the Packers.
b. Solely on the fans.
Question 12. The deadweight loss due to this tax will be:
a. Positive.
b. Equal to zero.
II. Multiple Choice Questions: (Worth 3 points each)
Question 13. Take the line given by the equation y = 2x + 3. Which of the following points (x, y) are on this line?
a. (1,5)
b. (5,1)
c. (2,3)
d. (3,2)
Question 14. Take the line described by the equation x = (1/2)(y – 3). Which of the following equations is parallel to this line, but has a y-intercept that is 1 unit greater than the original line?
a. y = 3x + 3
b. y = x + 3
c. y = 2x + 2
d. y = 2x + 4
Question 15. Given the Production Possibility Frontier below, at which point is the production efficient?
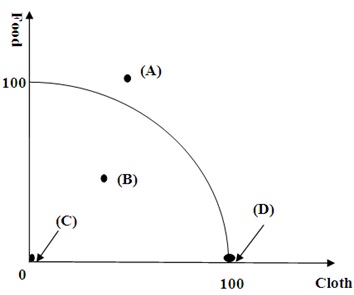
a. A
b. B
c. C
d. D
Question 16. Suppose Footland produces socks which it trades for leg warmers produced in Kneeland. Currently Footland trades 4 pair of socks for 1 set of leg warmers. Which of the following statements is certain to be true?
a. Footland has an absolute advantage in producing socks.
b. Footland’s opportunity cost of producing a pair of socks is less than or equal to ¼ a set of leg warmers.
c. Kneeland’s opportunity cost of producing a set of leg warmers is greater than or equal to 4 pairs of socks.
d. Kneeland’s opportunity cost of producing a pair socks is less than Footland’s opportunity cost of producing a pair of socks.
Use the following information to answer the next four (4) questions.
Suppose that John and Mike are farmers. They both have 200 days for working in one year. John can use one day of work to produce 1 ton of rice or 2 tons of wheat (or any combination of the two goods that lies on the straight line between these given combinations). Mike can use one day of work to produce 2 tons of rice or 5 tons of wheat (or any combination of the two goods that lies on the straight line between these given combinations). Assume that John and Mike both have linear production possibility frontiers.
Question 17. What is John’s opportunity cost of producing 5 tons of wheat?
a. 2 tons of rice
b. 0.5 ton of rice
c. 2.5 tons of rice
d. 10 tons of rice
Question 18. Which of the following statements is true?
a. John has both the absolute advantage and the comparative advantage in producing rice.
b. Mike has both the absolute advantage and the comparative advantage in producing rice.
c. John has the absolute advantage in producing rice and Mike has the absolute advantage in producing wheat.
d. John has the comparative advantage in producing rice and Mike has the comparative advantage in producing wheat.
Question 19. Suppose John and Mike are able to specialize and trade with each other. Which of the following prices for one ton of wheat is acceptable to both of them?
a. 0.15 tons of rice
b. 0.45 tons of rice
c. 0.75 tons of rice
d. 1 ton of rice
Question 20. Now assume that John adopts a new technology in rice production so that he can produce twice the original amount of rice a day, but his production of wheat does not change. Consider John’s Production Possibility Frontier. Let the y-axis represent wheat production and the x-axis represent rice production. Then, which of the following is true?
a. John’s new Production Possibility Frontier will be shift out from the origin but be parallel to his original production possibility frontier.
b. John’s new Production Possibility Frontier will shift in toward the origin but the y-intercept remains unchanged.
c. John’s new Production Possibility Frontier will shift out away from the origin but the y-intercept remains unchanged.
d. John’s new Production Possibility Frontier is the same as his original Production Possibility Frontier.
Question 21. Assume it takes Bob 5 hours to solve 20 Economics questions and it takes Bob 4 hours to solve 24 Physics questions. He has a total of 15 hours available. At which of the following combinations is Bob producing solutions efficiently?
a. 20 Economics solutions and 24 Physics solutions
b. 100 Economics solutions and no Physics solutions
c. 48 Economics solutions and 18 Physics solutions
d. 40 Economics solutions and 20 Physics solutions
Question 22. The Production Possibility Frontier for a firm producing only chairs and desks is shown below. Currently, the firm is producing at point P. What is the opportunity of producing 5 more chairs?
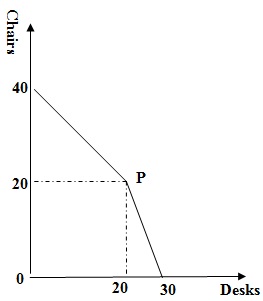
a. 1 desk
b. 5 desks
c. 0.5 desks
d. 2.5 desks
Use the following information to answer the next two (2) questions.
Tottiland can produce olive oil and tomatoes. If it produces only olive oil, it gets 40 gallons a day. If it produces only tomatoes, it can produce 50 pounds a day. It can also produce any linear combination in between these two points.
Question 23. What is the opportunity cost of one additional gallon of olive oil?
a. 1 pound of tomatoes
b. 4/5 pounds of tomatoes
c. 4 pounds of tomatoes
d. 5/4 pounds of tomatoes
Question 24. Suppose bad weather affects the production of tomatoes in Tottiland, and now it is only possible to get half as many pounds of tomatoes with the same amount of work as before. What is the opportunity cost of one additional gallon of olive oil?
a. The new opportunity cost of producing an additional gallon of olive oil is half the initial opportunity cost.
b. The new opportunity cost of producing an additional gallon of olive oil is twice the initial opportunity cost.
c. The opportunity cost of olive oil doesn’t change.
d. It is not possible to determine the change in the opportunity cost of producing an additional gallon of olive oil from the given information.
Question 25. What will happen to the equilibrium price and quantity in the market for hotdog buns if hotdogs become more expensive? The equilibrium price for hotdog buns will
a. Increase and the equilibrium quantity will decrease.
b. Increase and the equilibrium quantity will increase.
c. Decrease and the equilibrium quantity will decrease.
d. Decrease and the equilibrium quantity will increase.
Question 26. Which of the following statements is true?
a. Coffee and cream are complements. Holding everything else constant, when the price of coffee decreases, the demand for cream decreases.
b. Coffee and cream are complements. Holding everything else constant, when the price of coffee increases, the demand for cream decreases.
c. Coffee and tea are substitutes. Holding everything else constant, when the price of coffee increases, the demand for tea decreases.
d. Coffee and tea are substitutes. Holding everything else constant, when the price of coffee decreases, the demand for tea increases.
Question 27. Nintendo Wii is very popular among teenagers. When Nintendo releases a new version of the console that allows people to play video games and work out at the same time through its simulated interaction, Wii becomes very popular among retirees as well. Holding everything else constant, what will happen to the equilibrium price and quantity of Wii given this change?
a. The equilibrium quantity will increase, and the equilibrium price will increase.
b. The equilibrium quantity will increase, and the equilibrium price will decrease.
c. The equilibrium quantity will decrease, and the equilibrium price will increase.
d. The equilibrium quantity will decrease, and the equilibrium price will decrease.
Question 28. Gas prices continue to rise due to unrest in the Middle East and hurricane activity in the Gulf of Mexico. At the same time many people, concerned about potential terrorist threats, decide to avoid traveling by airplane. What will happen to the equilibrium price for airplane tickets and the equilibrium quantity of airplane tickets given this information? Assume that all airplane flights are identical and that there is only one market for airline tickets.
a. The equilibrium quantity of airplane tickets will increase, and the equilibrium price of airplane tickets will decrease.
b. The equilibrium quantity of airplane tickets will decrease, and the equilibrium price of airplane tickets will increase.
c. The equilibrium quantity of airplane tickets will decrease, and the effect of these changes on the equilibrium price of airplane tickets is indeterminate.
d. The equilibrium price of airplane tickets will increase, and the effect of these changes on the equilibrium quantity of airplane tickets is indeterminate.
Question 29. Which of the following statements are true?
I. Two goods are substitutes if the increase in the price of Good X causes an increase in the demand for Good Y.
II. Two goods are complements if the quantity demanded of Good A decreases when the price of Good B increases.
III. A good is a normal good if an increase in income causes the individual to demand less of this good.
a. Statement I is true.
b. Statement II is true.
c. Statements I and II are true.
d. Statements I, II and III are true.
Question 30. Suppose a market for bananas is composed of two consumers: Charles and Kim. Charles’s demand for bananas is given by QC = 15 – 3P, and Kim’s demand for bananas is given by QK = 5 - (1/2)P. Which of the following equations describes the market demand equation for the banana market?
a. The market demand curve can be derived by summing the demand function of Charles and Kim as Q = 20 - 4P for any price level.
b. The market demand curve will have two linear segments: Q = 5 - (1/2)P for prices between $5 and $10, and Q = 15 – 3P for prices between $5 and $0.
c. The market demand curve will have two linear segments: Q = 5 - (1/2)P for prices between $5 and $10; Q = 20 - (7/2)P for prices between $5 and $0.
d. The market demand curve will have two linear segments: Q = 5 - (1/2)P for prices between $5 and $10; Q = 20 - 4P for prices between $5 and $0.
Use the following information to answer the next four (4) questions.
The demand for skateboards is given by: PD = 38 – 6QD.
The supply of skateboards is given by: PS = 6 + 2QS.
Question 31. What is the equilibrium price (P) and equilibrium quantity (Q) in the market?
a. P=14, Q=4
b. P=10, Q=2
c. P=14, Q=6
d. P=15, Q=4
Now suppose that an excise tax of $8 per skateboard is placed on the producers of skateboards.
Question 32. What is the new equilibrium price, including the tax, (P) and equilibrium quantity (Q) in the market after the imposition of the tax?
a. P=8, Q=5
b. P=12, Q=3
c. P=22, Q=4
d. P=20, Q=3
Question 33. What is the amount of tax revenue generated from this tax?
a. $18
b. $32
c. $24
d. $8
Question 34. What is the deadweight loss resulting from the imposition of the tax?
a. $6
b. $4
c. $8
d. $24
Use the graph below to answer the following two (2) questions
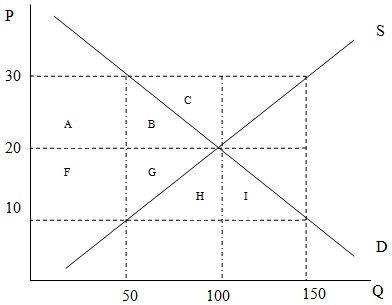
Question 35. Suppose that initially the above market is in equilibrium and the government decides to impose a maximum price of P=$10. The change in consumer surplus induced by this policy can be measured as a(n)
a. Increase of area F + area G + area H + area I
b. Decrease of areas F - area B
c. Increase of area F – area B
d. Increase of area F + area G- area B
Question 36. Suppose that initially the market is in equilibrium and the government decides to establish a price support at a price of P=$30. The cost to the government of this program, excluding any storage costs, is equal to
a. $1000
b. $1500
c. $2000
d. $3000
Question 37. Suppose you observe that the market for ice cream behaves as follows: If the price of a pint of ice cream is $10, the total quantity demanded is 40. When the price goes down to $5, the total quantity demanded is 45 pints. On the supply side, when the price of ice cream is $10 per pint, the total quantity supplied is 20. When the price of ice cream jumps to $20 per pint, the total quantity supplied is 30. Assume both the demand and the supply curves for ice cream are linear. If the government imposes a price ceiling of $15, what will happen in the market?
a. There will be a shortage of 20 pints of ice cream.
b. There will be a shortage of 10 pints of ice cream.
c. There will be a surplus of 10 pints of ice cream.
d. There will be a surplus of 20 pints of ice cream.