Discussion:
Aqueous Ionic Equilibrium
1- Consider the following titration curve of a weak acid titrated with strong base. At which point(s) on the graph is the solution a buffer?
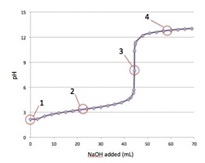
2- Which of the following solutions has the highest buffer capacity? Choose from:
0.100 M NaCl / 0.100 M NaOH
pure H2O
0.050 M NaCN / 0.050 M HCN
0.100 M HCl / 0.100 M NaOH
0.025 M NaCN / 0.025 M HCN
3- A student adds solid silver chloride (AgCl) to each of two beakers: one containing 1.0 L of pure water, and one containing 1.0 L of 0.500 M NaCl. In which will AgCl be more soluble, and why? Choose from:
0.500 M NaCl: the sodium ions in the solution will complex with the chloride, allowing more AgCl to dissolve.
0.500 M NaCl: in the 0.500 M NaCl solution, the chloride ions that are already present will increase the amount of AgCl that dissolves by decreasing the value of
Neither: AgCl is completely insoluble, and will not dissolve in either.
Pure H2O: in the 0.500 M NaCl solution the chloride ions that are already present will inhibit the AgCl from dissolving by increasing the value of Q.
Both: AgCl is freely soluble in both.
4- Determine the pH of each solution.
0.16M KCHO2
0.16M KCHO2
0.25M KI
5- Ammonia, NH3 , is a weak base with a K b value of 1.8×10 -5 .
What is the percent ionization of ammonia at this concentration?