Assignment Task:
Problem 1:
(a) A closed system containing steam at constant pressure, 250 bar, undergoes a reversible process, during which 450 kJ/kg of heat transfer takes place. The initial dryness fraction and temperature of steam are 1 and 412oC respectively. Determine:
(i) Its final specific enthalpy;
(ii) Its final temperature;
(iii) Its final specific internal energy.
(b) In the process of compression inside a gas engine, the work done on the gas piston is 110 kJ/kg and the heat rejection to the cooling water is 68 kJ/kg. Calculate the change in internal energy in kJ.
(c) Discuss, in details, one of the applications of the engineering thermodynamics principles in Building Services Engineering.
Problem 2:
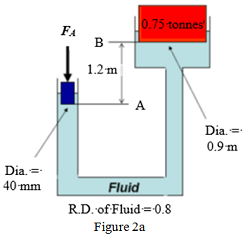
(a) A hydraulic machine is used to lift a load of 0.75 tonnes as shown in Figure 2a. Calculate the force, FA, required at the small piston.
(b) A jet of water from the nozzle is shown in Figure b.
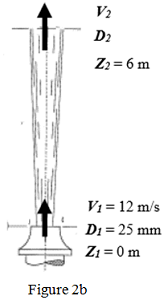
Assuming that the jet of water remains in circular shape and all losses of energy are neglected, determine:
(i) The velocity at the outlet, V2;
(ii) The diameter at the outlet, D2.
(c) Discuss, in details, the importance of fluid mechanics study in Building Services Engineering.
Problem 3:
(a) Sketch the Temperature - Specific Volume (T-v) Diagram for steam which shows clearly the regions of compressed liquid, mixture, superheated vapour, saturated liquid line, saturated vapour line and critical point.
(b) Water is a working fluid in a system. At state A, the absolute pressure is 2 bar and the specific volume is 0.7 m3/kg. Calculate the dryness fraction (quality) of water at state A.
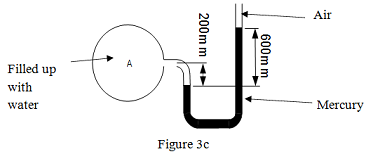
(c) A mercury U-tube manometer inserted into a water stream gives the readings as shown in Figure c. Determine the gauge pressure at A. (Hint: Relative density of mercury is 13.6)
Problem 4:
(a) An electrical circuit is shown in Figure a.
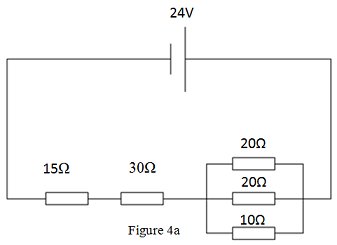
Calculate:
(i) The equivalent resistance, Req;
(ii) The total supply current, Is;
(iii) The current through the 10Ω resistor;
(iv) The potential difference across the 10Ω resistor.
(b) If two capacitors having capacitances of 6μF and 10μF are connected in series across a 200V supply, determine
(i) The potential difference across each capacitor.
(ii) The charge on each capacitor.
Problem 5:
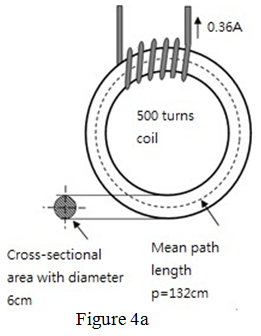
(a) A steel ring, with a mean circumference of 132 cm and a uniform cross-sectional area, is wound with a coil of 500 turns as shown in Figure 4a. Given that the permeability of free space μo = 4π x 10-7 T/(At/m) and the relative permeability of steel μr = 900. Determine:
(i) The magneto motive force (MMF) produced by the coil;
(ii) The average magnetic field strength (H) in the ring;
(iii) The average magnetic flux density (B) in the ring;
(iv) The total magnetic flux (Φ) in the ring.
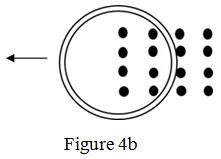
(b) A copper ring is moving to the left, while the magnetic field is pointing out of the paper in Figure b, determine:
(i) The direction of induced current flowing in the ring;
(ii) The direction of the induced current if the ring is moving out of the paper;
(iii) The direction of the induced current if the magnetic field is moving to the right.
(c) Discuss the effect of the induced current if the speed of the ring increases.
Problem 6:
(a) A baby was laid inside a cradle next to a wall. He was crying loudly and echo was heard after 0.01 second. Assuming that the speed of sound through air is 340 m/s, calculate the distance between the baby and the wall.
(b) The baby was then given a musical toy which causes resonating waves in an open- ended air column. The speed of sound through the air column is 340 m/s, the length of the air column is 0.5 m. Calculate the frequencies of the first harmonics.
(c) There were 2 babies inside the room, crying at 60dB and 70dB respectively. A split-type air-conditioner is also turned on and its sound pressure level is 79dB. Calculate the total sound pressure level inside the room.
(d) A domestic helper with a pair of earmuffs put over his ears entered the room and noticed that the sound intensity level received is significantly reduced. Explain, with reasons, the reduction in sound intensity level.
Problem 7:
(a) When a beam of light falls on a smooth and highly polished surface, the angle of incidence is 40o. Explain, with the assistance of diagram and relevant laws, the expected light ray and its pathway.
(b) Inside a classroom, a light source of 800 cd is placed above a 0.4 m2 meeting table. Assuming that the light source is located at a height of 2 m vertically from the floor and the height of the meeting table is 0.8 m,
(i) Find the value of illuminance, E, on the top of the meeting table;
(ii) Find the luminous flux, F, falls on the top of the meeting table.
(iii) Calculate the vertical distance between the light source and table if the lux level on the meeting table is required to be 500 lux.
Need A Reliable And Trustworthy Engineering Science Assignment Help Service In The Industry At Affordable Prices? Hire Qualified Tutors To Score Notable Grades With Ease!
Tags: Engineering Science Assignment Help, Engineering Science Homework Help, Engineering Science Coursework, Engineering Science Solved Assignments, Enthalpy Assignment Help, Enthalpy Homework Help, Internal Energy Assignment Help, Internal Energy Homework Help, Engineering Thermodynamics Assignment Help, Engineering Thermodynamics Homework Help, Total Magnetic Flux Assignment Help, Total Magnetic Flux Homework Help, Dryness Fraction Assignment Help, Dryness Fraction Homework Help
Attachment:- Engineering Science.rar