Problem 1. Consider the market for bananas. Doctors report that consuming two bananas a day result in significant declines in cancer risk. Simultaneously, people's incomes increase and bananas are a normal good. This will result in the equilibrium price of bananas
a. Increasing.
b. Decreasing.
c. Being indeterminate since two events are occurring simultaneously.
d. Remaining constant.
Use the following graph to answer the next two questions.
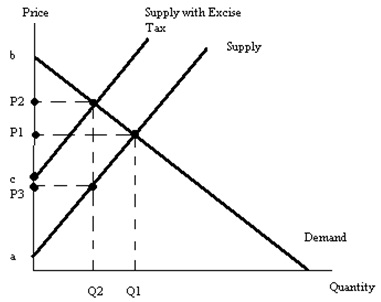
Problem 2. According to the graph the amount of the excise tax is best described as
a. P2 - P1
b. P1 - P3
c. c - a
d. P1 - a
Problem 3. To find the consumer tax incidence of this tax calculate the area of
a. (1/2)(P2 - P3)(Q1 - Q2)
b. (P2 - P3)(Q2)
c. (P2 - P3)(Q1 - Q2)
d. (P2 - P1)(Q2)
Answer the next two questions based on this information.
Consider a small closed economy that produces bicycles. In this economy the domestic demand for bicycles is given by P = 200 - Q while the domestic supply of bicycles is given by P = 20 + Q.
Problem 4. Suppose this economy opens to trade and the world price of bicycles is $150. Then this country will
a. Import bicycles from the world market.
b. Export bicycles to the world market.
Problem 5. Given the above information as well as the information in problem #4, when this economy opens to trade domestic consumer surplus in the market for bicycles will equal
a. $2500
b. $1250
c. $2250
d. $4050
Use the following information to answer the next two questions.
Suppose a market has two firms: Firm A and Firm B. The supply curve for Firm A is given by the equation P = Q while the supply curve for Firm B is given by the equation P = 2Q.
Problem 6. Suppose buyers are wiling to pay $10 per unit consumed. How many units will be supplied in this market at this price?
a. 10 units
b. 15 units
c. 20 units
d. 30 units
Problem 7. Which of the following equations represents the market supply curve?
a. P = 3Q
b. 2P = 3Q
c. P = (2/3)Q
d. P = (3/2)Q
Problem 8. A small country decides to open its markets to trade since it realizes that the world prices for the goods it produces are lower than the domestic prices for these goods. When this economy opens to trade
a. The domestic consumers in this economy benefit from this trade while the domestic producers in this economy are harmed.
b. The domestic producers in this economy benefit from this trade while the domestic consumers in this economy are harmed.
Problem 9. A small economy opens its markets to trade while at the same time it imposes a tariff. These decisions will
a. Provide benefits to domestic consumers but these benefits will be smaller than if the country remained a closed economy.
b. Provide benefits to domestic producers but these benefits will be smaller than if the country was simply an open economy.
c. Reduce the distributional consequences of opening this economy to trade.
d. Increase the distributional consequences of opening this economy to trade.
Problem 10. George always eats orange marmalade on his toast. Suppose that there is severe weather that damages this year's orange crop including the oranges that are used in making orange marmalade. Holding everything else constant, George will
a. Pay a higher price for each piece of toast and he will therefore consume fewer units of toast.
b. Pay a lower price for each piece of toast and he will therefore consume more units of toast.
c. Pay a higher price for each piece of toast and he will also consume more units of toast.
d. Pay a lower price for each piece of toast and he will consume fewer units of toast.