1. Using the following Fixed Basket of goods (Basket = 6 pizzas, 12 Tacos):
|
|
Pplzza
|
Ptacos
|
|
2010
|
$6.50
|
$2.80
|
|
2011
|
$7.90
|
$3.35
|
|
2012
|
$9.60
|
$3.90
|
|
2013
|
$11.00
|
$4.10
|
a) Calculate the Consumer Price Index (CPI) in each year.
b) Calculate the inflation rate from 2010 to 2011 and then from 2010 to 2013 using the calculated CPIs.
2. Using the economy below that produces only pizza and tacos:
|
|
Pplzza
|
QpIzza
|
Ptacos
|
Qtacos
|
Pwings
|
QwIngs
|
|
2010
|
$12.90
|
330
|
$12.50
|
590
|
$0.35
|
2000
|
|
2011
|
$13.80
|
475
|
$13.25
|
665
|
$0.55
|
2400
|
|
2012
|
$14.95
|
520
|
$14.75
|
765
|
$0.70
|
2590
|
|
2013
|
$15.20
|
600
|
$15.25
|
980
|
$1.05
|
2650
|
c) Calculate nominal GDP, real GDP (using 2010 as the base year), and the GDP deflator.
d) Calculate the inflation rate from 2010 to 2011 and then from 2010 to 2013.
3. Using the following Fixed Basket of goods (Basket = 7 pizzas, 15 Tacos, 50 wings):
Ppizza Ptacos Pwings
|
2010
|
$8.50
|
$1.20
|
$0.65
|
|
2011
|
$9.90
|
$2.00
|
$0.95
|
|
2012
|
$10.60
|
$3.50
|
$1.25
|
|
2013
|
$11.40
|
$3.90
|
$1.40
|
c) Calculate the Consumer Price Index (CPI) in each year.
d) Calculate the inflation rate from 2010 to 2011 and then from 2010 to 2013 using the calculated CPIs.
4. Name four supply and four demand shifters (for a total of 8 shifters) and explain in detail how a change in each will affect both price and quantity.
5. What are the three basic economic questions every economic system must answer regardless of its economic organization? Explain how each question is answered within the "circular flow diagram" of an economy?
6. Explain fully the difference between a pure public good, quasi-public good, private good and a common resource. Make sure you include the rival vs. non-rival and excludable vs. non-excludable characteristics of the goods.
7. Calculate the price elasticity of demand from a price increase from Pi to P2 for the following values:
P2 = $19.00
P1 = $16.00
Q1 = 1890
Q2 = 1470
8. Calculate the price elasticity of demand from a price decrease from P2t0 H for the following values:
P1= $55
P2 = $95
Q2 = 1280
Q1 = 1790
9. Calculate the income elasticity of demand for a good for an increase in income from l1 = $22,000 to l2 = $39,000 using the following Q values:
l1 = $22,000
l2 = $39,000
Q1 = 1150
Q2= 1162
10. Calculate the income elasticity of demand for a good for an increase in income from 11 = $22,000 to 12 = $39,000 using the following Q values:
11 = $22,000
12 = $39,000
Q1= 2100
Q2 = 2200
11. Calculate the income elasticity of demand for a good for an increase in income from 11 = $22,000 to 12 = $39,000 using the following Q values:
11 = $22,000
12 = $39,000
Q1 = 895
Q2 = 3350
12. Calculate the income elasticity of demand for a good for an increase in income from l1 = $22,000 to l2 = $39,000 using the following Q values:
l1 = $22,000
l2 = $39,000
Q1 = 110
Q2 = 125
13. Calculate the price elasticity of supply from a price increase from P1 to P2 for the following values:
P2 = $18.00
P1 = $16.80 Q1 = 1150
Q2 = 1780
14. Calculate the price elasticity of supply from a price decrease from P1 to P2 for the following values:
P2 = $1440
P1 = $1970
Q1 = 97800
Q2 = 12789
Use the following two Price Floor and Price Ceiling figures to answer question 15 and 16:
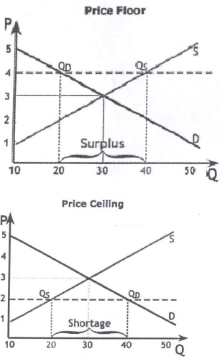
15. Using the Price Floor figure above calculate the before and after consumer surplus, producer surplus, and deadweight loss from the Price Floor.
16. Using the Price Ceiling figure above calculate the before and after consumer surplus, producer surplus, deadweight loss from the Price Ceiling.