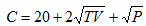1) This Christmas Bobo can either go on a Vegas Vacation (V), go on a road trip (R), or study Economics (E). He can also either have fun (F) or be sad (S) this Christmas. The joint pdf's for Bobo's Christmas are listed below:
|
Activity:
|
Vegas Vacation
|
Road Trip (R)
|
Economics
(E)
|
|
Fun (F)
|
0.16
|
0.24
|
0.4
|
|
Sad (S)
|
0.04
|
0.06
|
0.1
|
a) Calculate marginal pdf's of both variables (activity and utility).
b) Calculate the probability that Bobo has fun if Bobo studies economics (even though we all know it's impossible not to have fun with economics).
c) Calculate the probability that Bobo went on a road trip if we know he had fun over Christmas.
d) How do (b) and (c) help show that the two variables are statistically independent?
2) Every year, Coraline gets to roll her six-sided birthday die. Two of the sides give her $100 for her birthday, three of the sides give her $50 for her birthday, and one side gives her $10 for her birthday.
a) Calculate the expected value of Coraline's birthday die.
b) Calculate the variance of Coraline's birthday die.
3) Dr. Derivative can spend $10 or $80 on Halloween decorations, and get either 20 or 60 Trick-or-Treaters.
|
|
$10
|
$80
|
|
20
|
0.4
|
0.2
|
|
60
|
0.1
|
0.3
|
a) Calculate marginal pdf's of both variables
b) Calculate expected values of both variables
c) Calculate covariance. What does this mean?
4) Find the critical values for a 1 tail test where:
a) df=54 on a t distribution (0.5% in the tail)
b) df=27 on a Chi-Squared distribution (5% in the tail)
c) df1=8, df2=10 on an F distribution (1% in the tail)
5) Gangnam style parodies have an average humor of 75. Assuming a normal distribution and a standard deviation of 5, calculate:
a) The probability a random parody has a humor of greater than 87.
b) The cut-off humor value for the 20% worst parodies.
6) Use the following sample data for the next question:
|
Person
|
Etho
|
Guude
|
Boo
|
|
Awesomeness
|
12
|
8
|
4
|
|
Coolness
|
5
|
7
|
9
|
a) Calculate expected awesome and coolness.
b) Calculate variance in awesomeness and coolness.
c) Calculate covariance and correlation between awesomeness and coolness.
d) Calculate a 95% confidence interval for average coolness.
e) Use the data to estimate the following equation:
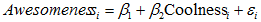
7) After a mental breakdown, you decide to make some changes to how many hours per week you spend on Recreation (R) and Family (F) in order to minimize your stress (S). The relationship between Stress, change in Recreational Life, and change in Family Life is expressed as:
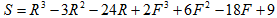
a) Assume that you can't make any changes to your Family life (F=0). Minimize your stress.
b) Assuming you can make any changes to recreation and family life, minimize your stress.
8) Consider the following relationship between campaign success (C), TV adds (TV) and Posters (P):
Assuming that TV adds cost $2,000 each, Posters cost $500 each, and a campaign has $12,000, maximize campaign success using the Lagrangean.