1. Suppose a country enacts a tax policy that discourages investment: suppose the policy reduces the investment rate immediately and permanently from S bar to s'.Assuming the economy starts in its initial steady state, use the Solow model to explain what happens to the economy over time and in the long run. Draw a graph showing how output evolves over time (put Yt on the vertical axis with a ratio scale, and time on the horizontal axis), and explain what happens to economic growth over time.
2. Suppose the level of TFP in an economy rises permanently from A to A'.
(a) Assuming the economy starts in its initial steady state, use the Solow model to explain what happens to the economy over time and in the long run.
(b) Draw a graph showing how output evolves over time, and explain what happens to the level and growth rate of per capita income.
(c) Suppose that A' grew at a constant rate, instead of being constant. Explain in words what you think would happen to GDP over time.
(d) How is the response of the economy to an increase in TFP different from the economy's response to an increase in the investment rate?
3. (a) Use the production function in equation () and the rules for computing growth rates: 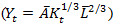 to write the growth rate of per capita GDP as a function of the growth rate of the capital stock. (Hint: Because the labor force is constant, the growth rates of GDP and per capita GDP are the same.)
to write the growth rate of per capita GDP as a function of the growth rate of the capital stock. (Hint: Because the labor force is constant, the growth rates of GDP and per capita GDP are the same.)
(b) Combine this result with the last equation in 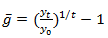 to get a solution for the growth rate of per capita GDP as a function of the current level of capital kt. Be sure to write your answer in terms of kt and parameters of the model only.
to get a solution for the growth rate of per capita GDP as a function of the current level of capital kt. Be sure to write your answer in terms of kt and parameters of the model only.
4. The table below reports per capita GDP and capital per person in the year 2007 for 10 countries. Your task is to fill in the missing columns of the table.
(a) Given the values in columns 1 and 2, fill in columns 3 and 4. That is, compute per capita GDP and capital per person relative to the U.S. values.
(b) in column 5, use the production model (with a capital exponent of 1/3) to compute predicted per capita GDP for each country relative to the United States, assuming there are no TFP differnces.
(c) In column 6, compute the level of TFP for each country that is needed to match up the model and the data. Comment on the general results you find.
5. The Black Death. In the middle of thefourteenth century, an epidemic known as the Black Death killed about a third of Europe'spopulation. While this was an enormous tragedy, over the next century wages are estimatedto have been higher than before the Black Death.
(a) Use the production model to explain why wages might have been higher.
(b) Can you attach a number to your explanation? In the model, by how much wouldwages rise if 1/3 of the population died from disease?