Ionic dissociation depends on the dielectric constant of the solvent.
The Arrhenius that ions are in aqueous solutions in equilibrium with parent molecular species allows many of the properties of ionic solutions to be understood. But difficulties began to arise after the initial acceptance of this ionic solution is to be understood. Ultimately the Arrhenius theory was attacked for the postulating molecules instead of ions in solutions of strong electrolytes. This was a dramatic reversal of the initial attacks on the Arrhenius theory which criticized it for postulating ions instead of undissolved molecules.
Refinements to the simplest ideas of the ionic solutions depend on the recognition of the role of the solvent and on the effect of interactions between the ions.
A remarkable feature of the Arrhenius electrolytic dissociation theory is that although it attributes the dissociation process to the solution of the electrolyte, it proceeds to ignore the role of the solvent. It treats the solvent as if it were an inert, ignorable medium. A detailed understanding of the molecular nature of ionic solutions must involve the very important role played by the solvent. It is necessary, for instance, to understand why water is a unique solvent for ionic systems.
The electrostatic force of attraction between ions of charge Z+ and Z- is given by Coulomb's law:
For vacuum: ƒ(r) = Z+Z-[e2/4∏ε0)]/r2
For medium of dielectric ε/ε0: ƒ(r) = Z+Z-[e2/4∏ε0)]/(ε/ε0)r2
With the numerical values for e2/4∏ε0, the second of this equation is:
ƒ (r) = (2.307 × 10-28) Z+Z-/(ε/ε0)r2
For water, the dielectric constant factor ε/ε0 has the very large value of about 80. The force of interaction and the energy required to overcome coulombic forces are thus smaller by almost of very low dielectric. The easy dissociation of electrolytes in aqueous solutions compared with gaseous or low phase dielectric material is therefore understandable in terms of the high dielectric constant of water. The initial criticisms raised against the Arrhenius theory for postulating the dissociation of electrolysis in solution, however, remain valid arguments against any theory postulating appreciable dissociation to form free ions insolvents of low dielectric constant.
Although the dielectric effect is a major factor for the formation of ionic species in aqueous solutions, it is not great enough to reduce the intermolecular interaction to the small values found for gas phase molecules. We must therefore produce that for all but extremely dilute solutions, ionic interactions will not produce behavior found at infinite dilutes.
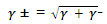
A similar treatment of the activities themselves leads, again for one to one electrolytes, to the mean activity 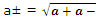
Extension of this property lets activities and their coefficients be defined for electrolytes beyond the AB type. An AB2 electrolyte would dissociate according to
AB2 = A2+ + 2B-
And the activity term that would appear in all thermodynamic treatments would be of form:
(aA2+) (aB-)2