An example illustrates the type of mechanism that can be written to explain the development of flash photolysis reactions.
Often, as the reactions in the ozone layer of the earth's atmosphere, we are interested in the kinetic behavior of species that are not available as on the shelf chemicals. The rate constants of reactions involving such species as H atoms, O atoms, and OH and HO2 radicals must be known if the dynamics of complex reaction mixtures are to be understood. Rate constant data can sometimes be obtained by generating such species by a high intensity short duration flash of light and then following their subsequent reaction. This approach is known as flash photolysis.
A typical flash used in such studies can generate about 1 mol of produces in the several microsecond duration of the flash. The amount of one or more of the products formed directly or indirectly, is usually determined by measuring the absorption of light at a suitable wavelength. As an illustration of this technique, studies of the formation and reaction of the perhydroxyl radical,H2O are described.
The two reactions are:
H2O = hv 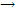 OH + H
OH + H
OH + H2 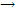 H2O + H
H2O + H
The formation of HO2 radicals by this flash photolysis route and studies of the kinetics of subsequent reactions has been reported†. The reaction system contained small amounts of H2Oand O2 and enough H2 to produce a total pressure of 1 atm. The formation of H atoms from the photolysis at water and their attachment to O2 to form HO2 occurred rapidly. Within about 10μs the intermediates, H and OH, were largely consumed. The kinetics of the subsequent reactions ofH2O radicals could then be studied.
The optional transmission at 210 nm, where HO2 absorbs, can be used to follow the decrease of this species. If the reaction that removes HO2 is second order in HO2, the H2O concentration will vary with the time according to:
1/c = 1/ c0 + kt
That the reaction is indeed order is confirmed by the linear relation for 1/ {log (I0 /i)}, which is proportional to 1/c, versus t, as shown in this order and the net product of the reaction, H2O2, suggest that the decay of H2O occurs by the reaction:
HO2 + HO2 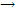 H2O2 + O2
H2O2 + O2
The reaction following the initial photolysis process can be changed by changing the reagents in the reaction system.
The principle reaction sequent system then is:
OH + HO2 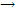 H2O + O2
H2O + O2
Principal reactions used for the simulation curves:
| Reaction |
Rate constant |
OH + H2 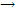 H2O + H H2O + H |
4 × 104 L mol-1 s-1 |
H + O2 H2 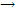 HO2 + H2 HO2 + H2 |
2 × 1010 L2 mol-2 s-1 |
H + O2 + Ar 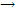 HO2 + Ar HO2 + Ar |
6 × 109 L2 mol-2 s-1 |
H + O2 + H2O 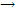 HO2 + H2O HO2 + H2O |
1.4 × 1011 L2 mol-2 s-1 |
HO2 + HO2  H2O2 H2O2 |
6 × 109 L mol-1 s-1 |
OH + HO2  H2O + O3 H2O + O3 |
1.2 × 1011 L mol-1 s-1 |