The boiling of a liquid may be defused by the temperature at which its vapour pressure which is equal to atmospheric pressure. The effect of addition in a non-volatile solute on the boiling point shown and its solution containing non-volatile solute with temperature are represented by the curves AB and CD respectively. It is evident by the curves temperature the vapour pressure of solutions is lower than that of the pure solvent and thus, the vapour pressure.
Curve for solution runs below that of the pure solvent. At temperature T0, the vapour pressure of the pure solvent becomes equal to the atmospheric pressure. Thus, the atmospheric pressure and therefore, it is necessary to heat the solution to a higher temperature sayT1 in the atmospheric pressure. Thus, it is clear that the solution in higher temperature than the pure solvent. Evidence T1 - T0 (or Δ Tb)is the elevation in boiling point vapour pressure (Δp), the elevation in the boiling point is also proportional to the solute concentration. Thus,
ΔTb ∝ Δp
According to Raoult's law, Δp ∝ xB
∴ ΔTb ∝ xB
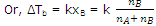
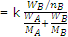

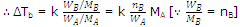
If WA is the mass of solvent in kg, then 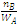 is equal to molality (m) of the solution
is equal to molality (m) of the solution
ΔTb = kMA m
Here, k and MA are constants and hence their product, i.e. kMA is replaced by another constant K2.
ΔTb = Kb m, where Kb is called boiling point-elevation constant or molal elevation constant or molal ebullioscopic constant.
As elevation in boiling point depends upon the relative number of moles of solute and solvent but does not depend upon the nature of solute, so it is a colligative property.