Freezing point of a substance is the temperature at which solid and liquid phases of the substance coexist. It is defined as the temperature at which its solid and liquid phases have the same vapour pressure.
The freezing point of a pure liquid is preset. Now, if a non-volatile solute is dissolved in the pure liquid to constitute a solution, there occurs a lowering in the freezing point. The freezing point of solution refers to the temperature at which the vapour pressure of the solvent in two phases, i.e. liquid solution and solid solvent is the same. Since the vapour pressure of the solvent at a lower temperature.
Evidently the freezing point of the pure solvent is the temperature corresponding to the point B (T0 K) and that of the solution is the temperature corresponding to the point A'(T1 K). Clearly, (T0 - T1) or ΔTƒ is the freezing point depression. Since its magnitude is determined by that of lowering of vapour pressure, the freezing point depression depends upon the molal concentration of the solute and does not depend upon the nature of solid. It is, thus, a colligative property. The general relation between these two quantities for a solution of non-electrolyte is usually expressed in term of molality of the solution
ΔTƒ ∝ Δp and Δp ∝ xB
∴ ΔTƒ = kxB =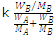
For dilute solution, 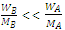 and hence,
and hence,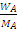 .
.
∴ ΔTƒ = k 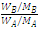 = k
= k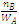 MA
MA
If WA is the mass of solvent in kg, then is equal to molality (m) of the solution
ΔTƒ = kMAm (? kMA = Kƒ)
∴ ΔTƒ =Kƒm, where Kƒ is called Freezing point depression constant or molal depression constant or cryoscopic constant.
As is clear from the above, depression in freezing point depends upon relative number of moles of solute and solvent but does not depend upon nature of solute, so it is a colligative property.