Average covalent radii can be assigned on the basis of molecular structures.
The accumulation of structural data by spectroscopic studies and both electron and x-ray diffraction studies allows one to investigate the possibility fo assigning a covalent bound molecule, i.e. of assigning a covalent radius to each atom. One begins by assigning half the length of a homonuclear bond as the covalent radius of the atoms forming the bond. Thus, from the equilibrium bond length of Cl2 of 199 pm, one obtains the value of 100 pm for the covalent radius of chlorine. From the carbon-carbon distance of 154 pm in ethane, for example, one obtains a value of 77 pm for the covalent radius of carbon and so forth. To proceed, one must now establish the extent to which the length of covalent bonds can be treated in terms of the sums of such covalent radii.
More extensive treatments of this type show that the bond lengths of many bonds are given within a few picometers by the sum of assigned atomic covalent radii. This suggests that covalent bonds have lengths sufficiently independent of factors other than the fixed radii for there to be some value in assigning radii to the bonded nuclei.
Some tests of additivity of covalent bond radii, pm:
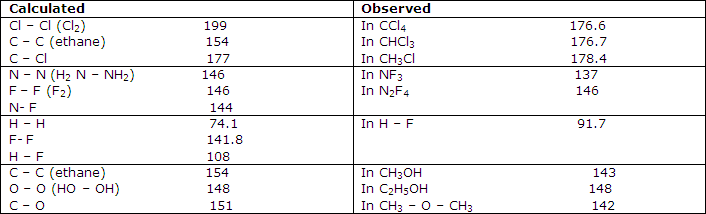
Further comparisons of these values with experimental results indicate, as shown in fact by some of the examples of table 1, that serious discrepancies can occur between simply predicted covalent-bond lengths and those observed. The C-F bond, for example, is calculated from the data of table 1 to have a length of 146 pm, whereas microwave spectral results forCH3F give it as 138.5 pm and electron-diffraction results for CF4 give 132 pm.
Such discrepancies led V. Schomaker and D. P. Stevenson to suggest that a bond length calculated from covalent radii must be adjusted for the difference in electronegativity of the bonded atoms. They suggested the relation:
rAB = rA + rB - 90 (xA - xB) r in pm
Some but not all, the interesting violations of simple covalent radii additivity are removed by this empirical expression. In other cases the Stevenson-Schomaker correction makes the agreement with the observed length pooper than that obtained by a simple addition of the covalent radii. Although a number of factors must be operating to affect the length of a bond between a pair of nuclei in any given molecule, the covalent radii of table 2 are often of value in estimating this bond length.
Covalent radii for atoms involved in single-bonded compounds, pm: