When the catalyst exists in a different phase than that of reactants, it is said to be heterogeneous catalyst, and the catalysis is called heterogeneous catalysis. For example, SO2 can be oxidized to SO3 using vanadium pentaoxide (V2O5) or platinum (Pt) as catalyst.
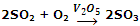
Here, V2O5 is solid, while the reaction reactants are gaseous. This reaction is employed during the manufacture of sulphuric acid by Contact Process.
In heterogeneous catalysis, the catalyst is generally solid while the reactants are gases and the reaction starts from the surface of the solid catalyst. That, is why heterogeneous catalysis is also is also called surface catalysis.
Some more examples of industrially important heterogeneous catalytic reactions are:
Manufacture of NH3 from N2 and H2 by Haber's process, using iron as catalyst.
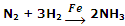
Manufacture of CH3OH from CO and H2 using (a mixture of Copper, ZnO and Cr2O3) as catalyst.
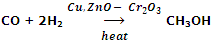
Oxidation of NH3 with O2 using Pt as catalyst in Ostwald process.
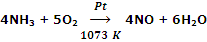
Oxidation of polluting gases such as CO and NO into non-toxic gases by the catalytic converter in the car's exhaust system. The catalytic converter consists of a mixture of transition metals such as platinum, palladium and rhodium. These catalysts oxidize CO and unburnt hydrocarbons to CO2 and H2O and reduce oxides of nitrogen to N2.
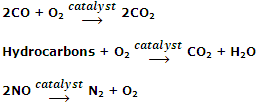
Hydrogenation of oils to form vegetable ghee using finely divided nickel as catalyst.

Polymerization of ethylene using TiCl3 and trialkyl aluminium (Ziegler-Natta method) as catalyst.