Alkyl halides or haloalkanes are the compounds in which a halogen is bonded to an alkyl group. They have the general formula RX (where R is alkyl group, CnH2n+1 and X is halogen atom). These may be obtained from an alkane by replacement of one hydrogen atom by a halogen atom.
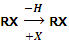
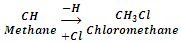
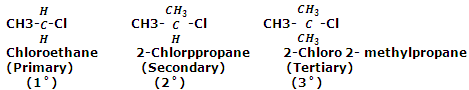
Alkyl halides are classified as primary, secondary and tertiary alkyl halides depending on whether the halogen atom is attached to a primary, secondary or tertiary carbon atom respectively. For example,
Halogen derivatives of unsaturated hydrocarbons: replacement of some hydrogen atom in alkenes or alkynes by some halogen atom yields this type of halogen compounds. Some ordinary examples are listed below:
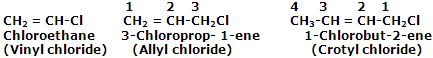
Aromatic halogen compound or haloarenes are the halogen compounds which contain at least one aromatic ring. Halogen derivatives of aromatic compounds can of two kinds:
Aryl halides: in these compounds, the halogen atom is directly combined to the carbon of benzene nucleus. They are also called nuclear substitution derivatives.
Aralkyl halides: in this type of compounds, halogen atom is linked to the carbon atom of the side chain. They are also called side chain substitution derivatives.
The side chain derivatives are very similar to aliphatic halogen derivatives i.e. haloalkanes.
The halides in which halogen atom is attached to an sp3-hybridised carbon atom next to a carbon-carbon double bond are known as allylic halides.
The halides in which halogen atom is attached to one of the carbon atoms of a carbon-carbon double bond (C=C) are known as vinylic halides.
The halides in which halogen atom is attached to a carbon atom next to aromatic ring are known as benzylic halides.
In alkyl halides, allyl halides and benzyl halides halogen atom is bonded to an sp3 hybridized carbon atom.
Alkyl, allylic and benzylic halides may be further be classified as primary, secondary and tertiary halides.
In aryl halides and vinyl halides halogens atom is bonded to an sp2 hybridized carbon atom.