Nucleophilic substitution reactions in halides containing - X bond may take place through either of the two different mechanisms,SN1 and SN2.
SN1 Mechanism (unimolecular Nucleophilic Substitution)
In this type, the rate of reaction dependent only on the concentration of alkyl halide, i.e.
Rate = k [RX]
The tertiary alkyl halides react by SN1 mechanism via formation of carbocations as intermediates as given below:
Step I: in the first step the alkyl halide slowly dissociates into halide and carbocation.
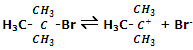
This step is the slowest and reversible. It involves the cleavage of C-Br bond for which the energy is obtained through salvation of halide ion with the proton of protic solvent. Since the rate of reaction depends upon the slowest step, the rate of reaction depends only on the concentration of alkyl halide and not on the concentration of nucleophile.
Step IInd: in the second step, carbocation at once combines with the nucleophile to form the final substituted product.
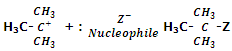
The order of reactivity of a variety of alkyl halides from SN1 mechanism is as below:
The 3+ alkyl halides are most reactive because the intermediate carbocation formed in their case is the most stable. The more stable intermediate is formed at faster rate.
SN2 Mechanism (Bimolecular Nucleophilic Substitution)
In this type of reaction is dependent on the concentration of alkyl halide as well as nucleophile, i.e.
Rate = k [RX] [Z-]
In this mechanism the incoming nucleophile interacts with alkyl halide causing the carbon-halide bond to break while forming a new carbon nucleophile bond. These two processes occurs at the same time in a single step and no intermediate is formed. As the reaction progresses and the bond between the nucleophile and the carbon atom starts forming and the bond between carbon atom and leaving group starts breaking. Finally, the product formed and the leaving group goes away.
In the transition state, the carbon atom is simultaneously bonded to incoming nucleophile and the leaving group. Such structures formed are unstable and cannot be isolated. This is due to the carbon atom in the transition state is at the same time bonded to five atoms and consequently is unstable.
The order of reactivity can be explained in terms of stability of transition state. Bulky alkyl groups attached to the carbon carrying halogen make the transition state unstable due to crowding (steric hindrance and decrease the reactivity of the alkyl halide through SN2mechanism. In 3° alkyl halide three alkyl groups are attached to the carbon carrying halogen. Therefore, transition state in this case has maximum energy and hence the reactivity is least. The 2° alkyl halides with two alkyl groups are most reactive whereas 1° alkyl halide with one alkyl group is most reactive.
Starting with an optically active alkyl halide, the reaction through SN2 mechanism results in complete inversion of configuration as it involves attack of nucleophile from backside. For example, when (-) -2-bromoethane is allowed to react with sodium hydroxide, (+)-2-octanol is formed. In (+)-2-octanol the position of -OH group is opposite to what bromide had occupied in (-)-2-bromooctane