These are polymers that can be broken into small segments by enzyme-catalysed reactions. The required enzymes are produced by microorganism. It is a known fact that the carbon-carbon bonds of chain growth polymers are inert to enzyme-catalysed reactions, and hence they are non biodegradable. To make such polymers biodegradable we have to insert certain bonds in the chains so that these can be easily broken by the enzymes. Now when such polymers are buried as waste, microorganisms present in the ground can degrade the polymer.
One of the most excellent methods of making a polymer biodegradable is by introducing hydrolysable ester group into the polymer.
For example if acetal is added to an alkene undergoing radical polymerisation, ester group will be inserted into the polymer.
The weak links in the polymer are susceptible to enzyme catalysed hydrolysis.
Aliphatic polyesters are one of the significant categories of biodegradable polymers. Some other examples of biodegradable polymers are described below:
(i) PHBV (Poly-hydroxybutrate-co- 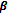 -hydroxy valerate): it is a copolymer of 3-hydroxy butyric acid and 3-hydroxypentanoic acid.
-hydroxy valerate): it is a copolymer of 3-hydroxy butyric acid and 3-hydroxypentanoic acid.
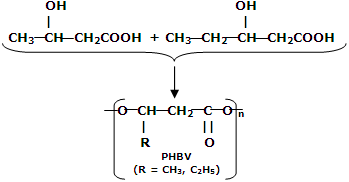
PHBV is used in orthopaedic devices and controlled drug release. The drug put in PHBV capsule is released after this polymer is degraded by enzymatic action. It can also be degraded by bacterial action.
(ii) Poly glycolic acid and poly lactic acid: these are also biodegradable polymers and are used for post operative stitches. These are bioabsorbable structures.
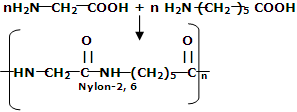
(iii) Nylon-2-Nylon: it is an alternating polyamide copolymer of glycine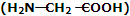 and amino caproic acid
and amino caproic acid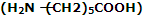 and is biodegradable.
and is biodegradable.