In common system, the aliphatic amines are named by using prefix for alkyl group followed by the word amine.
In case of mixed amines, the name of alkyl groups are arranged in alphabetical order. This is followed by the word amine. However, for simple secondary or tertiary amines another prefix di or tri is added before the name of the alkyl group.
There is yet another system of naming amines according to which they are called aminoalkanes. In this system, the secondary or tertiary amines are named as N-alkylaminoalkanes. In this case, the smaller alkyl groups are taken as subsequent on nitrogen atom of primary amine. For example,

In IUPAC system, the amines are considered to be amino derivatives of corresponding alkanes. Therefore, they are called alkanamines. These names are obtained by replacing e from the name of the parent alkane with suffix amine. The secondary and tertiary amines are, however, named as N-substituted derivatives of largest group of primary amines, i.e. N-Alkylalkanamines. The common and IUPAC names of some simple amines are given below in tabular form.
| Amine |
Common Name |
IUPAC Name |
| 1° Amines |
|
|
| CH3NH3 |
Methyl amine |
Methanamine |
| CH3CH2NH2 |
Ethyl amine |
Ethanamine |
| CH3CH2CH2NH2 |
n-Propyl amine |
Propan-1-amine |
| (CH3)2CHNH2 |
Iso-Propyl amine |
Propan-2-amine |
| 2° Amines |
|
|
| CH3 - NH - CH3 |
Dimethyl amine |
N-Methyl-methanamine |
| CH3 - NH - C2H5 |
Ethyl methyl amine |
N-Methyl-ethanamine |
| 3° Amines |
|
|
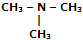 |
Tri-methyl amine |
N, N-Dimethyl-methanamine |
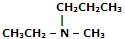 |
Ethyl methyl amine |
N-Ethyl-N-methyl-propanamine |
For compounds containing more than one amino group, a prefix di, tri, etc. is added before the suffix amine and the terminal e of the name of the hydrocarbon part is retained.
