Question:
1. Nancy is taking a course in Fairy Tales from Professor Grimm and another in Philosophy from Professor Par. In each course there will be two exams, a midterm exam and a final exam. In Professor Grimm's course, Nancy's grade will be determined by the minimum of her scores on the two exams. In Professor Par's course, the scores on the two exams are weighted equally. For each of the two courses, write thee different utility functions that describe Nancy's preference for scores on the midterm and the final exam. For each of the two courses, draw a diagram with a set of indifference curves for Nancy. Make sure to note higher and lower levels of utility.
1. Fairy Tales Course:
There are two options to get utility from: Mid term grades, and Final grades.
The utility function will take the form of:
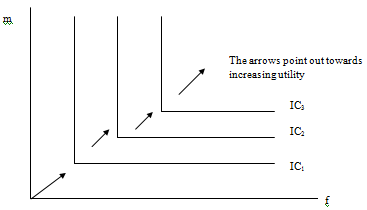
U (m, f) = min {m, f}
Where, m = mid term grades,
f = final exam grades
Indifference curves:
Philosophy Course:
There are two options to get utility from: Mid term grades, and Final grades.
The utility function will take the form of:
U (m, f) = 0.5m + 0.5f, since both the exams are equally weighed.
Where, m = mid term grades,
f = final exam grades
Indifference curves:
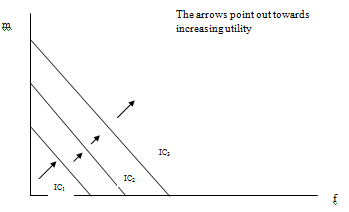
The indifference curves will be downwards sloping straight lines with slope -1. Here is the illustration:
U = 0.5m + 0.5f
- 0.5m = U - 0.5f
- m = 2U - f
Also, as the utility level increases, the intercept will increase, and the ICs will shift to right and up.