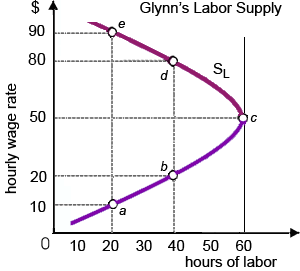
Glynn’s supply of labor is unitarily inelastic while the wage rate increases by: (1) $10 per hour to $20 per hour. (2) $10 per hour to $50 per hour. (3) $20 per hour to $50 per hour. (4) $20 per hour to $80 per hour. (5) $80 per hour to $90 per hour.
How can I solve my Economics problem? Please suggest me the correct answer.