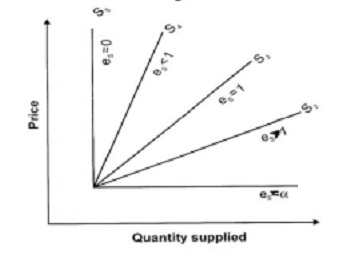
Types of elasticity of supply:
There are five kinds of elasticity of supply:
1. Perfectly elastic supply:
The coefficient of elasticity of supply is infinity. (i.e., es is ∞). For a little change or no alter in price, there will be an infinite amount of supply. (SS1 shown in figure below)
2. Relatively elastic supply:
The coefficient of elastic supply is always greater than 1(i.e., es > 1). Quantity supplied modifications by a bigger percentage than price. (SS2 shown in figure below)
3. Unitary elastic supply:
The coefficient of elastic supply is equivalent to 1 (i.e., es = 1). A change in cost will cause a proportionate modifications in quantity supplied. (SS3 shown in figure below)
4. Relatively inelastic supply:
The coefficient of elasticity is less than 1 (i.e., es < 1). Quantity supplied modifications by a lesser percentage than price. (SS4 shown in figure below)
5. Perfectly inelastic supply:
The coefficient of elasticity is equivalent to zero (i.e., es = 0).
The change in price will not bring around any modification in quantity supplied. (SS5 shown in figure below).