When the wholesale price P = $10 per bushel of peaches, it purely competitive peach orchard maximizes profit through producing ___ bushel of peaches at a total economic as profit or loss of $___. (i) zero; loss; -$4,000. (ii) 2000; loss; -$3,000. (ii) 3000; profit; $3,000. (iv) 4000; profit; $9,000. (v) 4000; profit; $4,000.
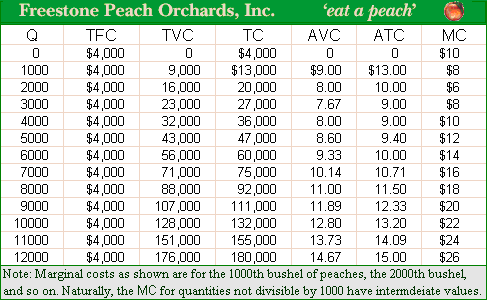
Can someone explain/help me with best solution about problem of Economics...