Assume, in the Kansas City grain market, total demands for wheat and the net supply of wheat per month are illustrates here:
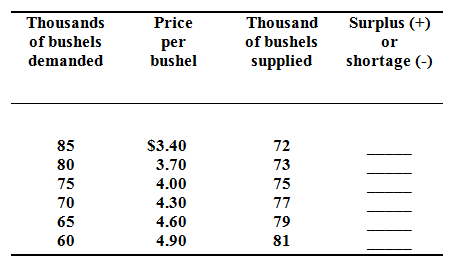
Why will $3.40 in this market not be the equilibrium price? Why not $4.90? “Surpluses drive prices up; shortages drive them down.” Do you agree?
Data from top to bottom: -13; -7; 0; +7; +14; and +21.