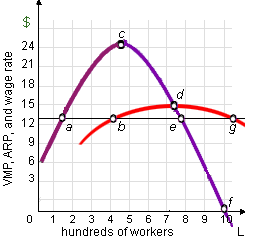
The firm in this illustrated graph is clearly: (1) price taker in the sale of its output because of the shapes of the VMP and MRP curves. (2) price taker in the purchase of labor when this can hire as several workers as this chooses at roughly of $13 per hour. (3) monopsonist since it should increase the wage rate to hire more labor. (4) monopolist since it should cut the price of its output to sell more product (5) polygamist.+
How can I solve my Economics problem? Please suggest me the correct answer.