Glynn’s preferences in between work and leisure give in a: (i) wealth effect that exceeds the leisure consequence above point c. (ii) weak preference for working more than 40 hours per week. (iii) substitution effect that exceeds the income effect at wage rates exceeding $50 per hour. (iv) strong aversion to working more than 40 hours weekly. (v) backward-bending [negatively-sloped] labor supply at hourly wage rates above $50.
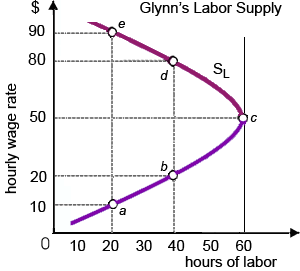
Please choose the right answer from above...I want your suggestion for the same.