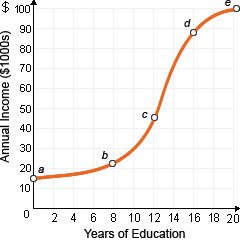
A currently-laid-off worker is probably to find another job quickly when the worker has substantial amounts of: (i) unemployment compensation and a strong union. (ii) specific human capital gained at the previous job. (iii) screening, signaling, and credentialing. (iv) general human capital from previous education and work experience. (v) savings accumulated from past income.
Hey friends please give your opinion for the problem of Economics that is given above.