Simplified demonstration of Little’s Law:
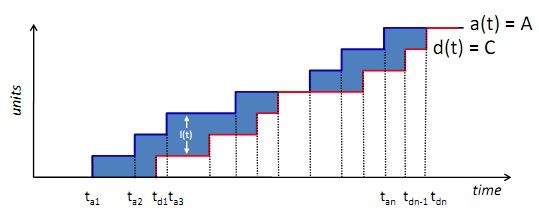
• a(t): the number of arrivals up to time t
• d(t): the number of departures up to t
• l(t) = a(t) –d(t) ≥ 0, the number of units in the system at time
• H(t): the area enclosed between the curves a(t) & d(t). represents the accumulated time in system during that interval measured in request-seconds (or request-minutes, etc.)
Simplified demonstration:
L ≡ H/T
R ≡ H/C
X ≡ C/T
H/T ≡ (C/T) (H/C);
L = X/R