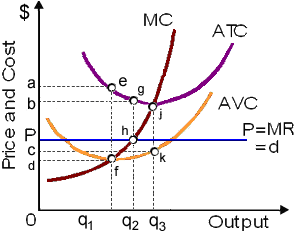
This figure in below is demonstrates the operations of a profit-maximizing pure competitor into the: (1) market period. (2) short run. (3) long run. (4) super long run since this can alter technology. (5) shutdown range of production.
Hey friends please give your opinion for the problem of Economics that is given above.