Determine into which of the following 3 kinds (A), (B) and (C) the matrices (a) to (e) beneath can be categorized:
Type (A): The matrix is in both reduced row-echelon form and row-echelon form.
Type (B): The matrix is in row-echelon form however not in decreased row-echelon form.
Type (C): The matrix is in neither reduced row-echelon form nor in row-echelon form.
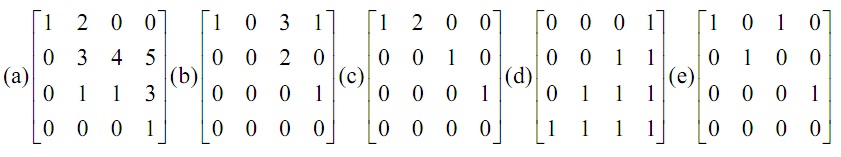
(f) Find all 2x3 reduced row-echelon matrices having a bottom row containing only zeros.