The entropy due to the rotational motion of the molecules of a gas can be calculated.
Linear molecules: as was pointed out, any rotating molecule has a set of allowed rotational energies. For a linear molecule the allowed rotational energies of a molecule of moment of inertia I are given approximated by
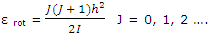
Furthermore, the number of states corresponding to a given value of J is given by 2J + 1. These features of the rotational energy patterns allow the rotational partition function to be deduced. This result can be used to obtain the rotational entropy contribution. The rotational contribution to the entropy, which must be added to the rotational contribution, is given by
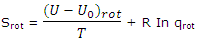
The partition function for rotation of a linear molecule obtained is
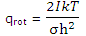
For a linear molecule, which has just 2 rotational degrees of freedom, the value of U - U0 for rotation was found, with this expression, to be RT. The rotational entropy of a diatomic or a linear polyatomic molecule can thus be written
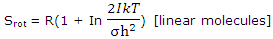
When numerical values are inserted for the constants, the rotational contributions of linear molecules to the entropy of ideal gases are given by
S°rot (J K-1 mol-1) = 877.37 + 8.3144 (In I + In T - In σ) [I in kg m2]
Example: calculate the 25°C rotational entropy of 1 mol of CO molecules. The moment of inertia of a CO molecule, measured by method given is 14.50 × 10-47 kg m2.
Solution: substitution in eq. and recognizing that σ = 1, gives
S°rot (J K-1 mol-1) = 877.37 + 8.3144[In (14.50 × 10-47) + In 298.15]
= 877.37 + 8.3144 (-105.55 + 5.70)
= 47.17 J K -1 mol-1
For comparison, the translational entropy of 1 mol of CO at 25°C and a pressure of 1 bar is calculated, to be 150.472 J K-1 mol-1.
The much greater translational entropy contribution (compared with the rotational entropy contribution) can be understood in terms of the much closer spacing of the translational energy levels and therefore the much larger number of translational states throughout which the molecules are distributed.
Nonlinear molecules: it is applicable to all diatomic molecules and all linear molecules. Generally shaped molecules, with 3 rather than 2 rotational degrees of freedom, require the use of 3/2 RTfor the rotational energy and the rotational partition function for nonlinear molecules given. For gases composed of such molecules
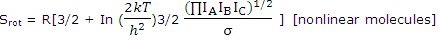
With numerical values this becomes
S°rot (J K-1 mol-1) = 1320.83 + 4.157 In IAIBIC + 12.471 In T - 8.3143 In σ [IA, IB, IC in kg m2]
Limitations: these equations cannot be applied to molecules with very low moments of inertia or at very low temperatures. In both cases the spacing of the energy levels becomes appreciable compared with the thermal energy, and the integration that produced, for example, is not valid.