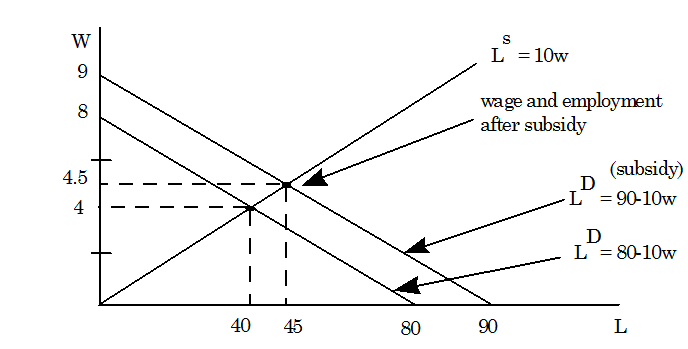
The U.S. Congress raised the minimum wage from $4.25 per hour to $5.15 per hour in the year of 1996. People suggested that a government subsidy could help employers finance the higher wage. Assume the supply of low-skilled labour is as
LS =10w
where LS is the quantity of low-skilled labour (in millions of persons employed each year) and w is the wage rate (in dollars per hour). The demand for labour is specified by
LD = 80-10w
Assume that rather than a minimum wage, the government pays a subsidy of $1 per hour for each employee. Determine total level of employment be now? And equilibrium wage rate be?
Let w indicate the wage received by the employee. Then the employer attaining the $1 subsidy per worker hour only pays w-1 for each worker hour. As illustrated in below Figure, the labor demand curve shifts to:
LD = 80 - 10 (w-1) = 90 - 10w,
Here w illustrate the wage received by the employee.
The new equilibrium will be specified by the intersection of the old supply curve along with the new demand curve, and thus, 90-10W** = 10W**, or W** = $4.5 per hour and L** = 10(4.5) = 45 million persons employed.