Quantities in a queuing system:
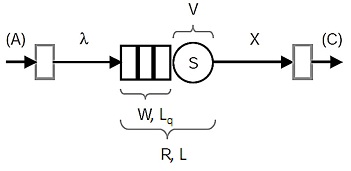
A: Count of arrivals into system throughout measurement period T
Ak: Count of arrivals into queue k throughout measurement period T
C: Count of global system completions throughout the period T
Ck: Count of completions which departed the queue k during T
Vk: Count of repeated visits to the server k throughout T
λk: Arrival rate at resource k = Ak / T
R: Mean time in system (residence time)
L: Average number of requests in system
W: Mean time in queue (that is, waiting time)
Lq: Average number of waiting to be served
S: Mean service time per completed job
X: Throughput
T: Total measurement period or observation time
K: Total number of queuing nodes k in system