Suppose that your utility, U, is a function only of wealth, Y, and that U(Y) is as drawn below. In this graph, note that U(Y) increases linearly between points a and b.
Suppose further that you do not know whether or not you will be sick, but you do know that the probability of becoming sick is p (while the probability of staying healthy is 1-p). If you do get sick, your wealth will be Ys = 0. If you do not get sick, your wealth will be Yh > 0.
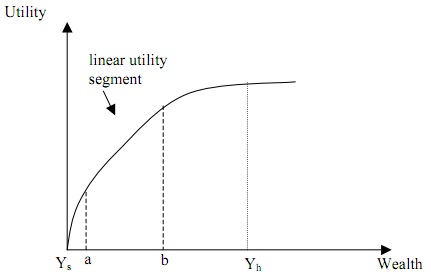
(1) Write an expression for expected income, EI, and an expression for expected utility without insurance.
(2) Assume that a < EI < b. Draw, on the graph above, a line showing expected utility without insurance. Also draw a line showing expected utility with actuarially fair full insurance.
(3) Consider an actuarially fair partial insurance contract that offers a if you are sick and b if you are healthy. Would your utility with such a contract be greater or less than your utility with an actuarially fair full insurance contract? Briefly, explain.