John Wong is a fresh graduate and has a limited amount of funds for investments. He expects that the Hong Kong stock market will fall soon but he is not familiar with derivatives. In order to gain more money to buy a car, he explores engaging in Hang Seng Index (HSI) options trading. After consulting his investment advisor, he considers HSI put options in the table below. As of the market closed on 24 August 2010, the Hang Seng Index was at 20659.
The information for Hang Seng Index put options as of 24 August 2010:
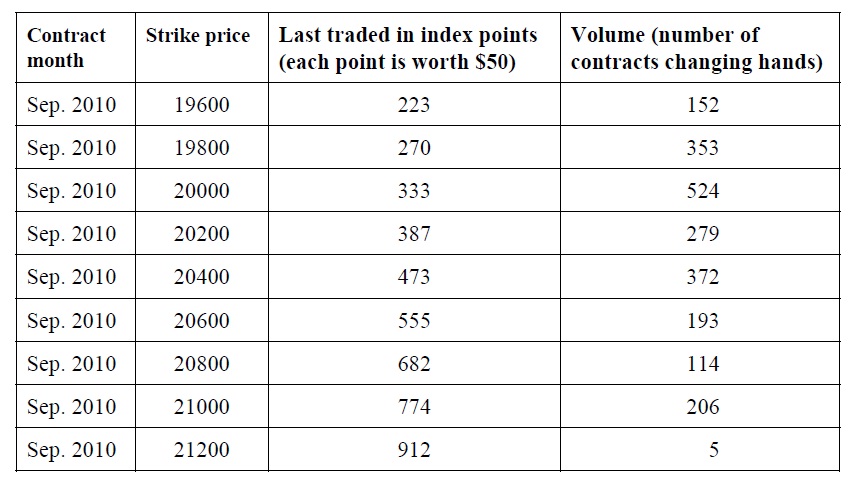
a) After reading the above table, John Wong realizes that HSI put options are very expensive for higher strike price put options. Please explain.
b) John Wong observes that the lower strike price options have a higher trading volume than higher strike price options. Please explain this phenomenon.
c) John Wong decides to focus on the HSI put option with the 20600 strike price. He is, however, not sure about the fair market price of the option. If the dividend yield of HSI constituent stocks is 3%, the Hong Kong interbank offered rate is 1%, the standard deviation of the HSI index return is 0.22, and the option has, for simplicity, one month to expire, what is the fair value of the put option using the Black-Scholes option pricing model? Show all your steps. Is the option price calculated the same as the market price shown in the table? If not, please explain the reason.
d) Under the Black-Scholes option pricing model, which factor do you think is the most difficult one to estimate? Discuss two methods to estimate the above factor and explain which method is the best.